Today, give a try to Techtonique web app, a tool designed to help you make informed, data-driven decisions using Mathematics, Statistics, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization. Here is a tutorial with audio, video, code, and slides: https://moudiki2.gumroad.com/l/nrhgb. 100 API requests are now (and forever) offered to every user every month, no matter the pricing tier.
In this post, we will test the overfitting (if it can overfit and when it stops; if a it works well with a reasonable number of hidden features) and scaling properties of nnetsauce.CustomRegressor. Scaling tests were made on Colab with GPU T4.
Installing packages
!pip install nnetsauce
!pip install mlsauce
Overfitting tests
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from tqdm import tqdm
# NOTE: This script requires nnetsauce to be installed
# Install with: pip install nnetsauce
try:
from nnetsauce import CustomRegressor
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: nnetsauce is not installed. Please install it with:")
print("pip install nnetsauce")
exit(1)
# Set random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
# Define a complex target function
def target_function(x):
"""Complex non-linear function to approximate"""
return np.sin(2 * np.pi * x) + 0.5 * np.sin(8 * np.pi * x) + 0.3 * np.cos(5 * np.pi * x)
# Generate training and test data
n_train = 50
n_test = 200
X_train = np.random.uniform(0, 1, n_train).reshape(-1, 1)
y_train = target_function(X_train.ravel()) + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, n_train)
X_test = np.linspace(0, 1, n_test).reshape(-1, 1)
y_test = target_function(X_test.ravel())
# Test different numbers of hidden features (nodes)
# CustomRegressor adds hidden layers to boost the base model's capacity
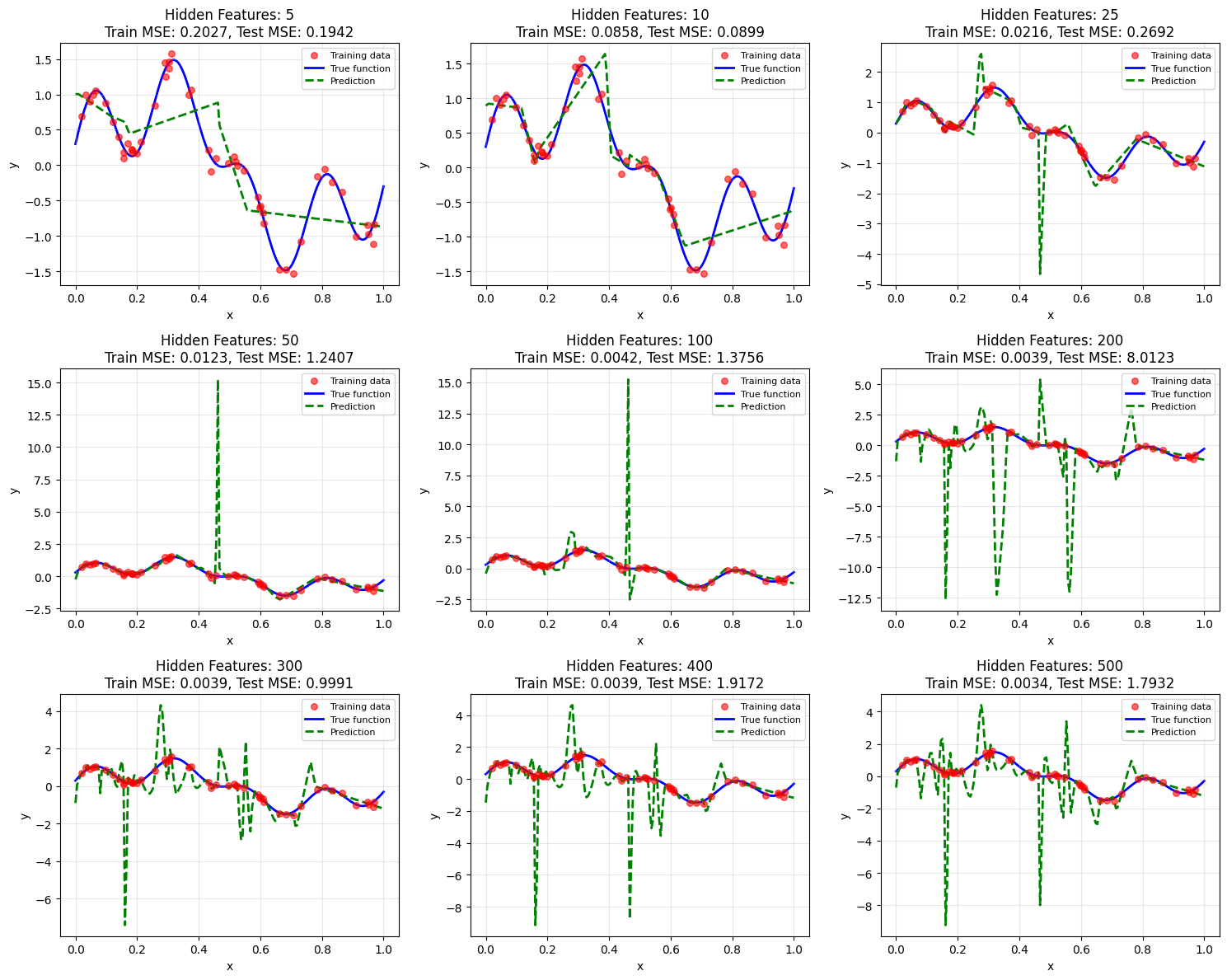
n_hidden_features_list = [5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
# Create figure with subplots - FIXED: Changed from 2x3 to 3x3 to accommodate 9 plots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(15, 12))
axes = axes.ravel()
train_errors = []
test_errors = []
for idx, n_hidden in tqdm(enumerate(n_hidden_features_list)):
# Create CustomRegressor with LinearRegression as base
# n_hidden_features controls model capacity
# activation_name='relu' uses ReLU activation for hidden features
model = CustomRegressor(
obj=LinearRegression(),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu', # or 'tanh', 'sigmoid'
nodes_sim='sobol', # quasi-random sampling
)
# Fit the model
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_train_pred = model.predict(X_train)
y_test_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# Calculate errors
train_mse = mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_pred)
test_mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred)
train_errors.append(train_mse)
test_errors.append(test_mse)
# Plot results
ax = axes[idx]
ax.scatter(X_train, y_train, c='red', s=30, alpha=0.6, label='Training data', zorder=3)
ax.plot(X_test, y_test, 'b-', linewidth=2, label='True function', zorder=1)
ax.plot(X_test, y_test_pred, 'g--', linewidth=2, label='Prediction', zorder=2)
ax.set_title(f'Hidden Features: {n_hidden}\nTrain MSE: {train_mse:.4f}, Test MSE: {test_mse:.4f}')
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.legend(loc='upper right', fontsize=8)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('nnetsauce_overfitting_demo.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("Saved: nnetsauce_overfitting_demo.png")
# Create a second figure showing error vs model capacity
fig2, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
# Plot MSE vs number of hidden features
ax1.plot(n_hidden_features_list, train_errors, 'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Training MSE')
ax1.plot(n_hidden_features_list, test_errors, 's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Test MSE')
ax1.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features (Model Capacity)', fontsize=12)
ax1.set_ylabel('Mean Squared Error', fontsize=12)
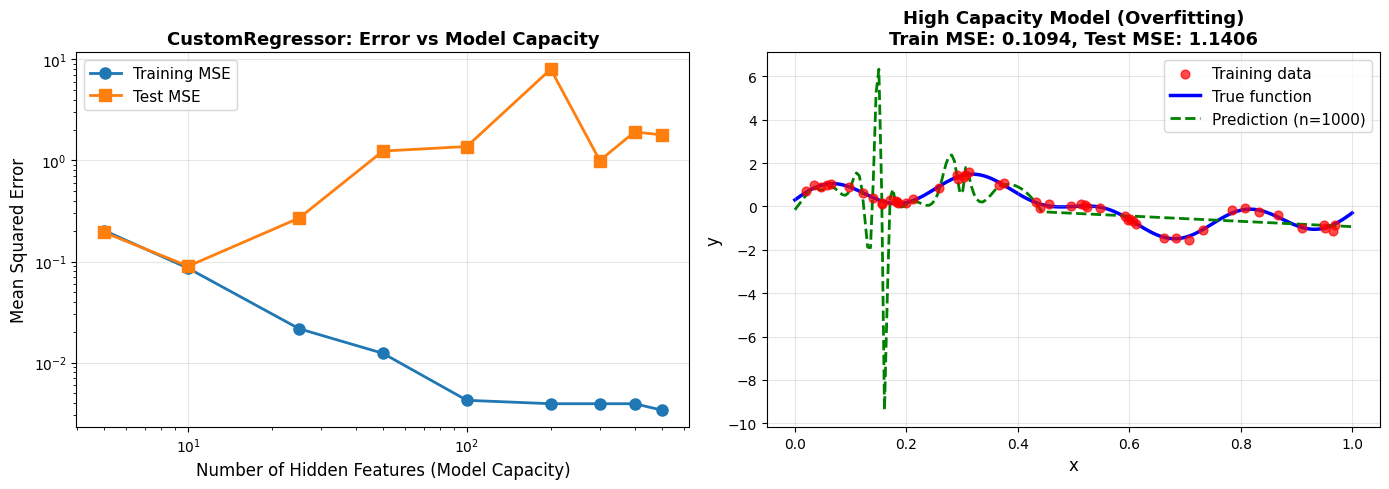
ax1.set_title('CustomRegressor: Error vs Model Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax1.legend(fontsize=11)
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax1.set_xscale('log')
ax1.set_yscale('log')
# Demonstrate overfitting with very high capacity
n_overfit = 1000
model_overfit = CustomRegressor(
obj=LinearRegression(),
n_hidden_features=n_overfit,
activation_name='relu',
a=0.01,
nodes_sim='sobol',
bias=True,
dropout=0.0,
n_clusters=0,
)
model_overfit.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_overfit = model_overfit.predict(X_train)
y_test_overfit = model_overfit.predict(X_test)
ax2.scatter(X_train, y_train, c='red', s=40, alpha=0.7, label='Training data', zorder=3)
ax2.plot(X_test, y_test, 'b-', linewidth=2.5, label='True function', zorder=1)
ax2.plot(X_test, y_test_overfit, 'g--', linewidth=2, label=f'Prediction (n={n_overfit})', zorder=2)
ax2.set_title(f'High Capacity Model (Overfitting)\nTrain MSE: {mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_overfit):.4f}, Test MSE: {mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_overfit):.4f}',
fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax2.set_xlabel('x', fontsize=12)
ax2.set_ylabel('y', fontsize=12)
ax2.legend(fontsize=11)
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('nnetsauce_error_analysis.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("Saved: nnetsauce_error_analysis.png")
# Print summary statistics
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("OVERFITTING DEMONSTRATION WITH NNETSAUCE")
print("="*60)
print("\nModel: CustomRegressor(LinearRegression) with ReLU activation")
print(f"Training samples: {n_train}")
print(f"Target function: sin(2πx) + 0.5·sin(8πx) + 0.3·cos(5πx)")
print("\n" + "-"*60)
print(f"{'Hidden Features':<15} {'Train MSE':<15} {'Test MSE':<15} {'Ratio':<10}")
print("-"*60)
for n_hidden, train_err, test_err in zip(n_hidden_features_list, train_errors, test_errors):
ratio = test_err / train_err if train_err > 0 else float('inf')
print(f"{n_hidden:<15} {train_err:<15.6f} {test_err:<15.6f} {ratio:<10.2f}")
print("-"*60)
print(f"\n✓ As model capacity increases, training error decreases")
print(f"✓ Overfitting occurs when test error > training error significantly")
print(f"✓ Training MSE improved from {train_errors[0]:.4f} to {train_errors[-1]:.4f}")
print(f"✓ Test/Train ratio shows overfitting severity")
# Calculate overfitting indicator
best_idx = np.argmin([test_err / train_err for test_err, train_err in zip(test_errors, train_errors)])
print(f"\n✓ Best generalization at {n_hidden_features_list[best_idx]} hidden features")
print(f" (Test/Train ratio = {test_errors[best_idx]/train_errors[best_idx]:.2f})")
print("="*60)
plt.show()
9it [00:00, 15.71it/s]
Saved: nnetsauce_overfitting_demo.png
Saved: nnetsauce_error_analysis.png
============================================================
OVERFITTING DEMONSTRATION WITH NNETSAUCE
============================================================
Model: CustomRegressor(LinearRegression) with ReLU activation
Training samples: 50
Target function: sin(2πx) + 0.5·sin(8πx) + 0.3·cos(5πx)
------------------------------------------------------------
Hidden Features Train MSE Test MSE Ratio
------------------------------------------------------------
5 0.202713 0.194247 0.96
10 0.085788 0.089940 1.05
25 0.021638 0.269249 12.44
50 0.012347 1.240659 100.48
100 0.004235 1.375602 324.85
200 0.003917 8.012315 2045.63
300 0.003917 0.999124 255.09
400 0.003917 1.917230 489.49
500 0.003388 1.793224 529.24
------------------------------------------------------------
✓ As model capacity increases, training error decreases
✓ Overfitting occurs when test error > training error significantly
✓ Training MSE improved from 0.2027 to 0.0034
✓ Test/Train ratio shows overfitting severity
✓ Best generalization at 5 hidden features
(Test/Train ratio = 0.96)
============================================================
Scaling tests on nnetsauce.CustomRegressor+Housing dataset
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from tqdm import tqdm
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# NOTE: This script requires nnetsauce and mlsauce to be installed
# Install with:
# pip install nnetsauce
# pip install git+https://github.com/Techtonique/mlsauce.git
try:
from nnetsauce import CustomRegressor
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: nnetsauce is not installed. Please install it with:")
print("pip install nnetsauce")
exit(1)
try:
import mlsauce as ms
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
print("WARNING: mlsauce is not installed. Will only compare with sklearn Ridge.")
print("To install: pip install git+https://github.com/Techtonique/mlsauce.git")
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = False
# Set random seed for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
# Load California housing dataset
print("Loading California housing dataset...")
housing = fetch_california_housing()
X, y = housing.data, housing.target
# Use a subset for faster computation
subset_size = 2000
indices = np.random.choice(X.shape[0], subset_size, replace=False)
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42
)
# Standardize features
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
print(f"\nDataset Info:")
print(f"Training samples: {X_train.shape[0]}")
print(f"Test samples: {X_test.shape[0]}")
print(f"Features: {X_train.shape[1]}")
print(f"Target: Median house value (in $100,000s)")
# Test different numbers of hidden features
n_hidden_features_list = [5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
# Store results
results = {
'sklearn_ridge': {'train_mse': [], 'test_mse': [], 'train_r2': [], 'test_r2': []},
}
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
results['mlsauce_ridge'] = {'train_mse': [], 'test_mse': [], 'train_r2': [], 'test_r2': []}
print("\n" + "="*70)
print("COMPARING SKLEARN RIDGE VS MLSAUCE RIDGEREGRESSOR")
print("="*70)
# Train models with different capacities
for idx, n_hidden in tqdm(enumerate(n_hidden_features_list),
total=len(n_hidden_features_list),
desc="Training models"):
# 1. CustomRegressor with sklearn Ridge
model_sklearn = CustomRegressor(
obj=Ridge(alpha=1.0),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_sklearn.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred_sk = model_sklearn.predict(X_train)
y_test_pred_sk = model_sklearn.predict(X_test)
results['sklearn_ridge']['train_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_pred_sk))
results['sklearn_ridge']['test_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred_sk))
results['sklearn_ridge']['train_r2'].append(r2_score(y_train, y_train_pred_sk))
results['sklearn_ridge']['test_r2'].append(r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred_sk))
# 2. CustomRegressor with mlsauce RidgeRegressor (if available)
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
model_mlsauce = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="cpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_mlsauce.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred_ml = model_mlsauce.predict(X_train)
y_test_pred_ml = model_mlsauce.predict(X_test)
results['mlsauce_ridge']['train_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_train, y_train_pred_ml))
results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred_ml))
results['mlsauce_ridge']['train_r2'].append(r2_score(y_train, y_train_pred_ml))
results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_r2'].append(r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred_ml))
# Create visualization
n_plots = 2 if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE else 1
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, n_plots, figsize=(7*n_plots, 10))
if n_plots == 1:
axes = axes.reshape(-1, 1)
# Plot 1: sklearn Ridge - MSE
ax = axes[0, 0]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn_ridge']['train_mse'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Training MSE', color='#2E86AB')
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn_ridge']['test_mse'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Test MSE', color='#A23B72')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features (Model Capacity)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Mean Squared Error', fontsize=12)
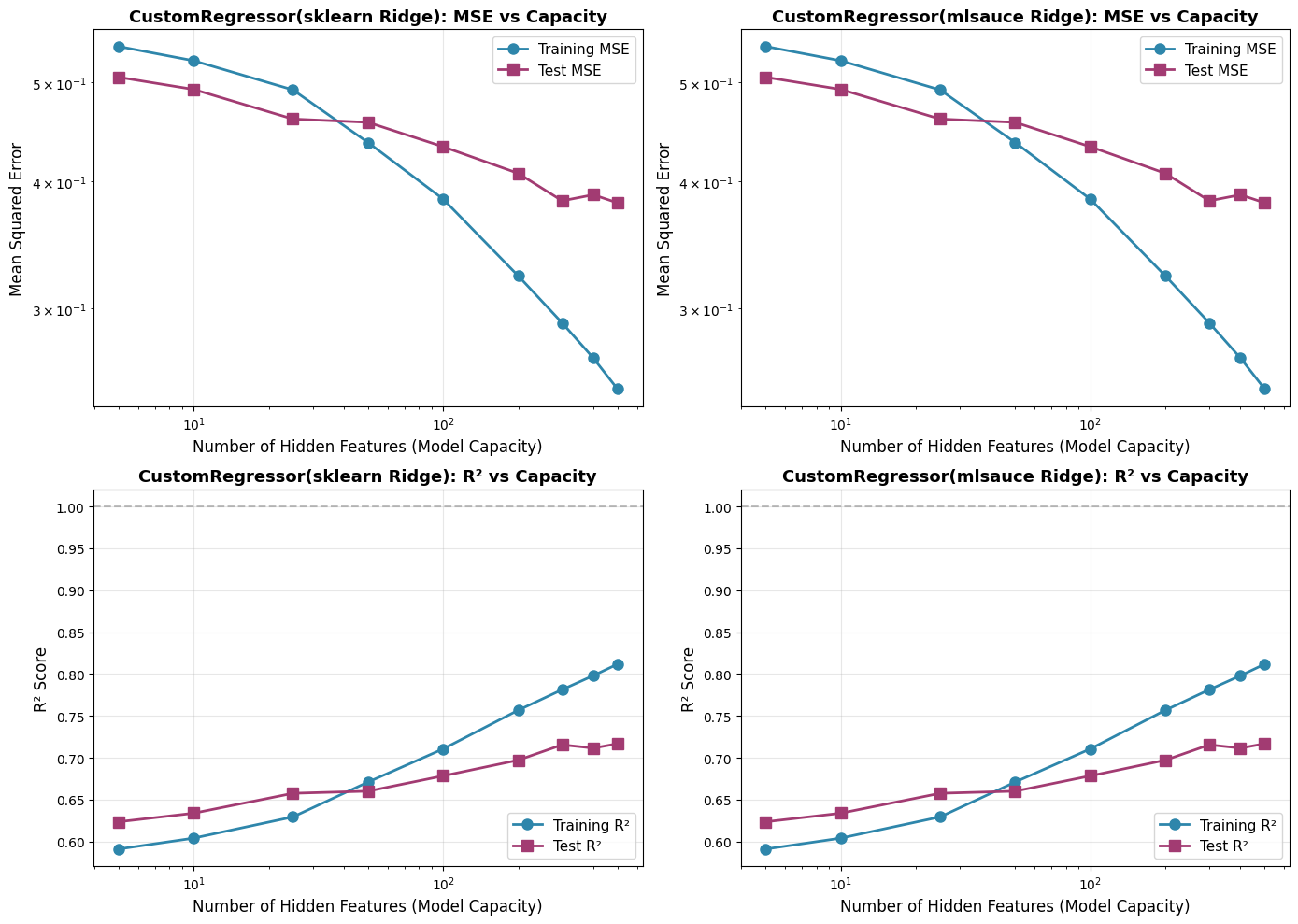
ax.set_title('CustomRegressor(sklearn Ridge): MSE vs Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
# Plot 2: sklearn Ridge - R²
ax = axes[1, 0]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn_ridge']['train_r2'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Training R²', color='#2E86AB')
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn_ridge']['test_r2'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Test R²', color='#A23B72')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features (Model Capacity)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('R² Score', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('CustomRegressor(sklearn Ridge): R² vs Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.axhline(y=1.0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
# Plot 3: mlsauce Ridge - MSE
ax = axes[0, 1]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_ridge']['train_mse'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Training MSE', color='#2E86AB')
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_mse'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Test MSE', color='#A23B72')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features (Model Capacity)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Mean Squared Error', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('CustomRegressor(mlsauce Ridge): MSE vs Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
# Plot 4: mlsauce Ridge - R²
ax = axes[1, 1]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_ridge']['train_r2'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Training R²', color='#2E86AB')
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_r2'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='Test R²', color='#A23B72')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features (Model Capacity)', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('R² Score', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('CustomRegressor(mlsauce Ridge): R² vs Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=11)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.axhline(y=1.0, color='gray', linestyle='--', alpha=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('california_housing_comparison.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("\nSaved: california_housing_comparison.png")
# Print comparison table
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("RESULTS COMPARISON: CALIFORNIA HOUSING DATASET")
print("="*100)
print("\n" + "-"*100)
print(f"{'N_Hidden':<12} {'sklearn Ridge':<40} {'mlsauce Ridge':<40}")
print(f"{'Features':<12} {'Train MSE':<12} {'Test MSE':<12} {'Test R²':<12} {'Train MSE':<12} {'Test MSE':<12} {'Test R²':<12}")
print("-"*100)
for i, n_hidden in enumerate(n_hidden_features_list):
sk_train_mse = results['sklearn_ridge']['train_mse'][i]
sk_test_mse = results['sklearn_ridge']['test_mse'][i]
sk_test_r2 = results['sklearn_ridge']['test_r2'][i]
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
ml_train_mse = results['mlsauce_ridge']['train_mse'][i]
ml_test_mse = results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_mse'][i]
ml_test_r2 = results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_r2'][i]
print(f"{n_hidden:<12} {sk_train_mse:<12.4f} {sk_test_mse:<12.4f} {sk_test_r2:<12.4f} "
f"{ml_train_mse:<12.4f} {ml_test_mse:<12.4f} {ml_test_r2:<12.4f}")
else:
print(f"{n_hidden:<12} {sk_train_mse:<12.4f} {sk_test_mse:<12.4f} {sk_test_r2:<12.4f} "
f"{'N/A':<12} {'N/A':<12} {'N/A':<12}")
print("-"*100)
# Summary statistics
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("SUMMARY")
print("="*100)
for model_name, model_results in results.items():
print(f"\n{model_name.upper().replace('_', ' ')}:")
best_test_idx = np.argmin(model_results['test_mse'])
best_r2_idx = np.argmax(model_results['test_r2'])
print(f" ✓ Best Test MSE: {model_results['test_mse'][best_test_idx]:.4f} at {n_hidden_features_list[best_test_idx]} hidden features")
print(f" ✓ Best Test R²: {model_results['test_r2'][best_r2_idx]:.4f} at {n_hidden_features_list[best_r2_idx]} hidden features")
# Calculate overfitting ratio
ratios = [test/train if train > 0 else float('inf')
for test, train in zip(model_results['test_mse'], model_results['train_mse'])]
best_ratio_idx = np.argmin(ratios)
print(f" ✓ Best generalization (lowest Test/Train MSE ratio): {ratios[best_ratio_idx]:.2f} at {n_hidden_features_list[best_ratio_idx]} hidden features")
# Detect overfitting
overfit_indices = [i for i, r in enumerate(ratios) if r > 2.0]
if overfit_indices:
print(f" ⚠ Overfitting detected (ratio > 2.0) at: {[n_hidden_features_list[i] for i in overfit_indices]} hidden features")
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("DIRECT COMPARISON")
print("="*100)
# Compare final performance
sk_final_test_mse = results['sklearn_ridge']['test_mse'][-1]
ml_final_test_mse = results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_mse'][-1]
sk_best_test_mse = min(results['sklearn_ridge']['test_mse'])
ml_best_test_mse = min(results['mlsauce_ridge']['test_mse'])
print(f"\nAt highest capacity (500 hidden features):")
print(f" sklearn Ridge Test MSE: {sk_final_test_mse:.4f}")
print(f" mlsauce Ridge Test MSE: {ml_final_test_mse:.4f}")
print(f" Winner: {'mlsauce' if ml_final_test_mse < sk_final_test_mse else 'sklearn'}")
print(f"\nBest overall performance:")
print(f" sklearn Ridge Best Test MSE: {sk_best_test_mse:.4f}")
print(f" mlsauce Ridge Best Test MSE: {ml_best_test_mse:.4f}")
print(f" Winner: {'mlsauce' if ml_best_test_mse < sk_best_test_mse else 'sklearn'}")
print("\n" + "="*100)
plt.show()
Loading California housing dataset...
Dataset Info:
Training samples: 1400
Test samples: 600
Features: 8
Target: Median house value (in $100,000s)
======================================================================
COMPARING SKLEARN RIDGE VS MLSAUCE RIDGEREGRESSOR
======================================================================
Training models: 100%|██████████| 9/9 [00:02<00:00, 3.38it/s]
Saved: california_housing_comparison.png
====================================================================================================
RESULTS COMPARISON: CALIFORNIA HOUSING DATASET
====================================================================================================
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
N_Hidden sklearn Ridge mlsauce Ridge
Features Train MSE Test MSE Test R² Train MSE Test MSE Test R²
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5 0.5428 0.5062 0.6235 0.5428 0.5062 0.6235
10 0.5255 0.4924 0.6337 0.5255 0.4924 0.6337
25 0.4919 0.4605 0.6575 0.4919 0.4605 0.6575
50 0.4366 0.4570 0.6601 0.4366 0.4570 0.6601
100 0.3841 0.4325 0.6783 0.3841 0.4325 0.6783
200 0.3228 0.4072 0.6972 0.3228 0.4072 0.6972
300 0.2902 0.3826 0.7154 0.2902 0.3826 0.7154
400 0.2679 0.3878 0.7115 0.2679 0.3878 0.7115
500 0.2498 0.3808 0.7167 0.2498 0.3808 0.7167
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
====================================================================================================
SUMMARY
====================================================================================================
SKLEARN RIDGE:
✓ Best Test MSE: 0.3808 at 500 hidden features
✓ Best Test R²: 0.7167 at 500 hidden features
✓ Best generalization (lowest Test/Train MSE ratio): 0.93 at 5 hidden features
MLSAUCE RIDGE:
✓ Best Test MSE: 0.3808 at 500 hidden features
✓ Best Test R²: 0.7167 at 500 hidden features
✓ Best generalization (lowest Test/Train MSE ratio): 0.93 at 5 hidden features
====================================================================================================
DIRECT COMPARISON
====================================================================================================
At highest capacity (500 hidden features):
sklearn Ridge Test MSE: 0.3808
mlsauce Ridge Test MSE: 0.3808
Winner: mlsauce
Best overall performance:
sklearn Ridge Best Test MSE: 0.3808
mlsauce Ridge Best Test MSE: 0.3808
Winner: mlsauce
====================================================================================================
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from time import time
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# NOTE: This script requires nnetsauce and mlsauce
try:
from nnetsauce import CustomRegressor
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: nnetsauce is not installed.")
exit(1)
try:
import mlsauce as ms
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
print("WARNING: mlsauce is not installed.")
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = False
# Set random seed
np.random.seed(42)
# Load dataset
print("Loading California housing dataset...")
housing = fetch_california_housing()
X, y = housing.data, housing.target
# Use larger subset to see performance differences
subset_size = 5000
indices = np.random.choice(X.shape[0], subset_size, replace=False)
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
# Split and scale
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42
)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
print(f"\nDataset: {X_train.shape[0]} training samples, {X_test.shape[0]} test samples")
print(f"Features: {X_train.shape[1]}")
# Configuration
n_hidden_features_list = [50, 100, 200, 500, 1000]
results = {
'sklearn': {'times': [], 'test_mse': []},
}
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
results['mlsauce_cpu'] = {'times': [], 'test_mse': []}
results['mlsauce_gpu'] = {'times': [], 'test_mse': []}
print("\n" + "="*70)
print("PERFORMANCE COMPARISON: SKLEARN VS MLSAUCE (CPU/GPU)")
print("="*70)
for n_hidden in n_hidden_features_list:
print(f"\nTesting with {n_hidden} hidden features...")
# 1. sklearn Ridge (CPU)
start = time()
model_sklearn = CustomRegressor(
obj=Ridge(alpha=1.0),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_sklearn.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = model_sklearn.predict(X_test)
elapsed_sklearn = time() - start
results['sklearn']['times'].append(elapsed_sklearn)
results['sklearn']['test_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred))
print(f" sklearn Ridge (CPU): {elapsed_sklearn:.3f}s")
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
# 2. mlsauce Ridge (CPU)
start = time()
model_mlsauce_cpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="cpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_mlsauce_cpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = model_mlsauce_cpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_cpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_cpu']['times'].append(elapsed_ml_cpu)
results['mlsauce_cpu']['test_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred))
print(f" mlsauce Ridge (CPU): {elapsed_ml_cpu:.3f}s (speedup: {elapsed_sklearn/elapsed_ml_cpu:.2f}x)")
# 3. mlsauce Ridge (GPU) - if available
try:
start = time()
model_mlsauce_gpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="gpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_mlsauce_gpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = model_mlsauce_gpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_gpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'].append(elapsed_ml_gpu)
results['mlsauce_gpu']['test_mse'].append(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_test_pred))
print(f" mlsauce Ridge (GPU): {elapsed_ml_gpu:.3f}s (speedup: {elapsed_sklearn/elapsed_ml_gpu:.2f}x)")
except Exception as e:
print(f" mlsauce Ridge (GPU): FAILED ({str(e)[:50]}...)")
results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'].append(None)
results['mlsauce_gpu']['test_mse'].append(None)
# Visualization
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 5))
# Plot 1: Training Time
ax = axes[0]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn']['times'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='sklearn Ridge (CPU)', color='#2E86AB')
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_cpu']['times'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='mlsauce Ridge (CPU)', color='#F18F01')
if any(t is not None for t in results['mlsauce_gpu']['times']):
valid_indices = [i for i, t in enumerate(results['mlsauce_gpu']['times']) if t is not None]
valid_n_hidden = [n_hidden_features_list[i] for i in valid_indices]
valid_times = [results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'][i] for i in valid_indices]
ax.plot(valid_n_hidden, valid_times,
'^-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='mlsauce Ridge (GPU)', color='#C73E1D')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Training Time (seconds)', fontsize=12)
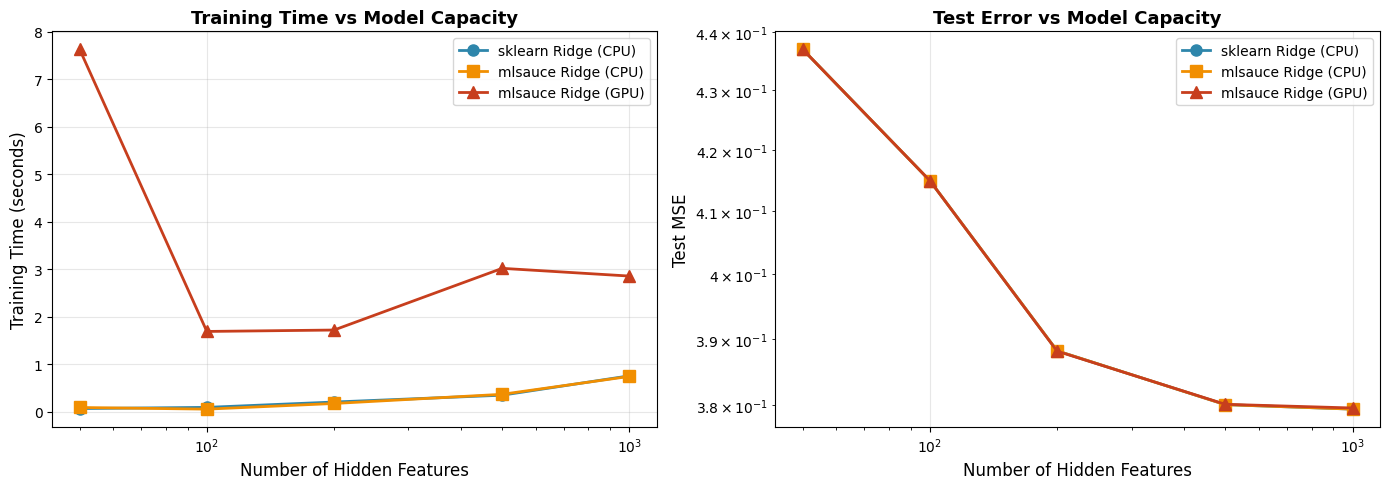
ax.set_title('Training Time vs Model Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=10)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
# Plot 2: Test MSE
ax = axes[1]
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['sklearn']['test_mse'],
'o-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='sklearn Ridge (CPU)', color='#2E86AB')
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
ax.plot(n_hidden_features_list, results['mlsauce_cpu']['test_mse'],
's-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='mlsauce Ridge (CPU)', color='#F18F01')
if any(t is not None for t in results['mlsauce_gpu']['test_mse']):
valid_indices = [i for i, t in enumerate(results['mlsauce_gpu']['test_mse']) if t is not None]
valid_n_hidden = [n_hidden_features_list[i] for i in valid_indices]
valid_mse = [results['mlsauce_gpu']['test_mse'][i] for i in valid_indices]
ax.plot(valid_n_hidden, valid_mse,
'^-', linewidth=2, markersize=8, label='mlsauce Ridge (GPU)', color='#C73E1D')
ax.set_xlabel('Number of Hidden Features', fontsize=12)
ax.set_ylabel('Test MSE', fontsize=12)
ax.set_title('Test Error vs Model Capacity', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
ax.legend(fontsize=10)
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('performance_comparison.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("\n\nSaved: performance_comparison.png")
# Summary table
print("\n" + "="*90)
print("PERFORMANCE SUMMARY")
print("="*90)
print(f"\n{'N_Hidden':<12} {'sklearn (CPU)':<20} {'mlsauce (CPU)':<20} {'mlsauce (GPU)':<20}")
print(f"{'Features':<12} {'Time (s)':<20} {'Time (s)':<20} {'Time (s)':<20}")
print("-"*90)
for i, n_hidden in enumerate(n_hidden_features_list):
sk_time = results['sklearn']['times'][i]
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
ml_cpu_time = results['mlsauce_cpu']['times'][i]
ml_gpu_time = results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'][i] if results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'][i] else 0
if ml_gpu_time:
print(f"{n_hidden:<12} {sk_time:<20.3f} {ml_cpu_time:<20.3f} {ml_gpu_time:<20.3f}")
else:
print(f"{n_hidden:<12} {sk_time:<20.3f} {ml_cpu_time:<20.3f} {'N/A':<20}")
else:
print(f"{n_hidden:<12} {sk_time:<20.3f} {'N/A':<20} {'N/A':<20}")
print("-"*90)
if MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE:
# Calculate average speedups
cpu_speedups = [sk_t / ml_t for sk_t, ml_t in
zip(results['sklearn']['times'], results['mlsauce_cpu']['times'])]
print(f"\nAverage mlsauce CPU speedup: {np.mean(cpu_speedups):.2f}x")
gpu_times_valid = [t for t in results['mlsauce_gpu']['times'] if t is not None]
if gpu_times_valid:
gpu_speedups = [sk_t / ml_t for sk_t, ml_t in
zip(results['sklearn']['times'][:len(gpu_times_valid)], gpu_times_valid)]
print(f"Average mlsauce GPU speedup: {np.mean(gpu_speedups):.2f}x")
print(f"GPU vs CPU speedup: {np.mean([c/g for c, g in zip(results['mlsauce_cpu']['times'][:len(gpu_times_valid)], gpu_times_valid)]):.2f}x")
print("\n" + "="*90)
print("\nNote: GPU acceleration is most beneficial with:")
print(" - Large datasets (10,000+ samples)")
print(" - High-dimensional features")
print(" - Large number of hidden features")
print(" - Multiple iterations/cross-validation")
print("="*90)
plt.show()
Loading California housing dataset...
Dataset: 3500 training samples, 1500 test samples
Features: 8
======================================================================
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON: SKLEARN VS MLSAUCE (CPU/GPU)
======================================================================
Testing with 50 hidden features...
sklearn Ridge (CPU): 0.069s
mlsauce Ridge (CPU): 0.091s (speedup: 0.76x)
mlsauce Ridge (GPU): 7.625s (speedup: 0.01x)
Testing with 100 hidden features...
sklearn Ridge (CPU): 0.094s
mlsauce Ridge (CPU): 0.057s (speedup: 1.65x)
mlsauce Ridge (GPU): 1.691s (speedup: 0.06x)
Testing with 200 hidden features...
sklearn Ridge (CPU): 0.206s
mlsauce Ridge (CPU): 0.176s (speedup: 1.17x)
mlsauce Ridge (GPU): 1.721s (speedup: 0.12x)
Testing with 500 hidden features...
sklearn Ridge (CPU): 0.350s
mlsauce Ridge (CPU): 0.369s (speedup: 0.95x)
mlsauce Ridge (GPU): 3.018s (speedup: 0.12x)
Testing with 1000 hidden features...
sklearn Ridge (CPU): 0.757s
mlsauce Ridge (CPU): 0.745s (speedup: 1.02x)
mlsauce Ridge (GPU): 2.856s (speedup: 0.27x)
Saved: performance_comparison.png
==========================================================================================
PERFORMANCE SUMMARY
==========================================================================================
N_Hidden sklearn (CPU) mlsauce (CPU) mlsauce (GPU)
Features Time (s) Time (s) Time (s)
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
50 0.069 0.091 7.625
100 0.094 0.057 1.691
200 0.206 0.176 1.721
500 0.350 0.369 3.018
1000 0.757 0.745 2.856
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Average mlsauce CPU speedup: 1.11x
Average mlsauce GPU speedup: 0.11x
GPU vs CPU speedup: 0.11x
==========================================================================================
Note: GPU acceleration is most beneficial with:
- Large datasets (10,000+ samples)
- High-dimensional features
- Large number of hidden features
- Multiple iterations/cross-validation
==========================================================================================
GPU only for RidgeRegressor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from time import time
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
try:
from nnetsauce import CustomRegressor
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: nnetsauce is not installed.")
exit(1)
try:
import mlsauce as ms
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
print("WARNING: mlsauce is not installed.")
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = False
exit(1)
print("="*80)
print("LARGE-SCALE GPU BENCHMARK")
print("Simulating the PDF example: 10,000 samples × 100 features")
print("="*80)
# Configuration matching the PDF's large-scale example
np.random.seed(42)
# Test different dataset sizes
dataset_configs = [
(1000, 50, "Small: 1K samples × 50 features"),
(5000, 100, "Medium: 5K samples × 100 features"),
(10000, 100, "Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example)"),
(20000, 150, "XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features"),
]
n_hidden = 100 # Fixed hidden features
results = {
'config': [],
'sklearn_cpu': [],
'mlsauce_cpu': [],
'mlsauce_gpu': [],
'gpu_speedup': [],
}
print("\nRunning benchmarks...\n")
for n_samples, n_features, description in dataset_configs:
print(f"\n{'='*80}")
print(f"{description}")
print(f"{'='*80}")
# Generate synthetic data
print(f"Generating {n_samples:,} samples with {n_features} features...")
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, n_features)
y = np.random.randn(n_samples)
# Split
split = int(0.8 * n_samples)
X_train, X_test = X[:split], X[split:]
y_train, y_test = y[:split], y[split:]
results['config'].append(description)
# 1. sklearn Ridge (CPU)
print("\n1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...")
start = time()
model_sklearn = CustomRegressor(
obj=Ridge(alpha=1.0),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_sklearn.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_sklearn.predict(X_test)
elapsed_sklearn = time() - start
results['sklearn_cpu'].append(elapsed_sklearn)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_sklearn:.3f}s")
# 2. mlsauce Ridge (CPU)
print("2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...")
start = time()
model_mlsauce_cpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="cpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
backend='cpu',
)
model_mlsauce_cpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_mlsauce_cpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_cpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_cpu'].append(elapsed_ml_cpu)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_ml_cpu:.3f}s")
print(f" Speedup vs sklearn: {elapsed_sklearn/elapsed_ml_cpu:.2f}x")
# 3. mlsauce Ridge (GPU)
print("3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...")
try:
start = time()
model_mlsauce_gpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="gpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
backend='cpu'
)
model_mlsauce_gpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_mlsauce_gpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_gpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_gpu'].append(elapsed_ml_gpu)
speedup = elapsed_sklearn / elapsed_ml_gpu
results['gpu_speedup'].append(speedup)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_ml_gpu:.3f}s")
print(f" Speedup vs sklearn: {speedup:.2f}x")
print(f" Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: {elapsed_ml_cpu/elapsed_ml_gpu:.2f}x")
if speedup > 1.0:
print(f" ✓ GPU IS FASTER!")
else:
print(f" ✗ GPU overhead still dominates")
except Exception as e:
print(f" FAILED: {str(e)[:60]}...")
results['mlsauce_gpu'].append(None)
results['gpu_speedup'].append(None)
# Visualization
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 6))
# Plot 1: Absolute times
x_pos = np.arange(len(results['config']))
width = 0.25
ax1.bar(x_pos - width, results['sklearn_cpu'], width,
label='sklearn Ridge (CPU)', color='#2E86AB', alpha=0.8)
ax1.bar(x_pos, results['mlsauce_cpu'], width,
label='mlsauce Ridge (CPU)', color='#F18F01', alpha=0.8)
gpu_times = [t if t is not None else 0 for t in results['mlsauce_gpu']]
ax1.bar(x_pos + width, gpu_times, width,
label='mlsauce Ridge (GPU)', color='#C73E1D', alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_ylabel('Training Time (seconds)', fontsize=12)
ax1.set_title('Training Time Comparison', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax1.set_xticks(x_pos)
ax1.set_xticklabels([c.split(':')[0] for c in results['config']], rotation=15, ha='right')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# Add value labels on bars
for i, v in enumerate(results['sklearn_cpu']):
ax1.text(i - width, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
for i, v in enumerate(results['mlsauce_cpu']):
ax1.text(i, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
for i, v in enumerate(gpu_times):
if v > 0:
ax1.text(i + width, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# Plot 2: Speedup factors
valid_speedups = [s if s is not None else 0 for s in results['gpu_speedup']]
colors = ['green' if s > 1.0 else 'red' for s in valid_speedups]
bars = ax2.bar(x_pos, valid_speedups, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax2.axhline(y=1.0, color='black', linestyle='--', linewidth=2, label='Break-even (1.0x)')
ax2.set_ylabel('GPU Speedup vs sklearn CPU', fontsize=12)
ax2.set_title('GPU Speedup Factor (>1.0 = GPU wins)', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax2.set_xticks(x_pos)
ax2.set_xticklabels([c.split(':')[0] for c in results['config']], rotation=15, ha='right')
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
ax2.legend()
# Add value labels
for i, (bar, val) in enumerate(zip(bars, valid_speedups)):
if val > 0:
label = f'{val:.2f}x'
y_pos = val + 0.05 if val > 1.0 else val - 0.1
ax2.text(i, y_pos, label, ha='center', va='bottom' if val > 1.0 else 'top',
fontweight='bold', fontsize=10)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("\n\nSaved: large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png")
# Summary table
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("BENCHMARK SUMMARY")
print("="*100)
print(f"\n{'Configuration':<40} {'sklearn CPU':<12} {'mlsauce CPU':<12} {'mlsauce GPU':<12} {'GPU Speedup':<12}")
print("-"*100)
for i, config in enumerate(results['config']):
sk = results['sklearn_cpu'][i]
ml_cpu = results['mlsauce_cpu'][i]
ml_gpu = results['mlsauce_gpu'][i]
speedup = results['gpu_speedup'][i]
gpu_str = f"{ml_gpu:.3f}s" if ml_gpu else "N/A"
speedup_str = f"{speedup:.2f}x" if speedup else "N/A"
print(f"{config:<40} {sk:<12.3f}s {ml_cpu:<12.3f}s {gpu_str:<12} {speedup_str:<12}")
print("-"*100)
# Key insights
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("KEY INSIGHTS")
print("="*100)
gpu_wins = [i for i, s in enumerate(results['gpu_speedup']) if s and s > 1.0]
if gpu_wins:
print(f"\n✓ GPU becomes advantageous at:")
for i in gpu_wins:
speedup = results['gpu_speedup'][i]
print(f" - {results['config'][i]}: {speedup:.2f}x speedup")
else:
print("\n✗ GPU did not outperform CPU in any configuration tested")
print(" Reasons:")
print(" - GPU overhead (data transfer, compilation) > computation time")
print(" - Dataset still too small to amortize GPU setup costs")
print("\n💡 For GPU to be beneficial, you typically need:")
print(" 1. Dataset: 50,000+ samples (PDF showed 1M+ data points)")
print(" 2. Multiple iterations (cross-validation, hyperparameter tuning)")
print(" 3. Batch predictions (forecasting 100+ time series simultaneously)")
print(" 4. High-dimensional features (200+)")
print(" 5. Deep architectures (multiple hidden layers)")
print("\n" + "="*100)
================================================================================
LARGE-SCALE GPU BENCHMARK
Simulating the PDF example: 10,000 samples × 100 features
================================================================================
Running benchmarks...
================================================================================
Small: 1K samples × 50 features
================================================================================
Generating 1,000 samples with 50 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.135s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.142s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.95x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 0.136s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.99x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 1.04x
✗ GPU overhead still dominates
================================================================================
Medium: 5K samples × 100 features
================================================================================
Generating 5,000 samples with 100 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.805s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.576s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.40x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 0.514s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.56x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 1.12x
✓ GPU IS FASTER!
================================================================================
Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example)
================================================================================
Generating 10,000 samples with 100 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 1.025s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.963s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.06x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 0.966s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.06x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 1.00x
✓ GPU IS FASTER!
================================================================================
XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features
================================================================================
Generating 20,000 samples with 150 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 2.896s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 2.875s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.01x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 3.563s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.81x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 0.81x
✗ GPU overhead still dominates
Saved: large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png
====================================================================================================
BENCHMARK SUMMARY
====================================================================================================
Configuration sklearn CPU mlsauce CPU mlsauce GPU GPU Speedup
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Small: 1K samples × 50 features 0.135 s 0.142 s 0.136s 0.99x
Medium: 5K samples × 100 features 0.805 s 0.576 s 0.514s 1.56x
Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example) 1.025 s 0.963 s 0.966s 1.06x
XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features 2.896 s 2.875 s 3.563s 0.81x
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
====================================================================================================
KEY INSIGHTS
====================================================================================================
✓ GPU becomes advantageous at:
- Medium: 5K samples × 100 features: 1.56x speedup
- Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example): 1.06x speedup
💡 For GPU to be beneficial, you typically need:
1. Dataset: 50,000+ samples (PDF showed 1M+ data points)
2. Multiple iterations (cross-validation, hyperparameter tuning)
3. Batch predictions (forecasting 100+ time series simultaneously)
4. High-dimensional features (200+)
5. Deep architectures (multiple hidden layers)
====================================================================================================
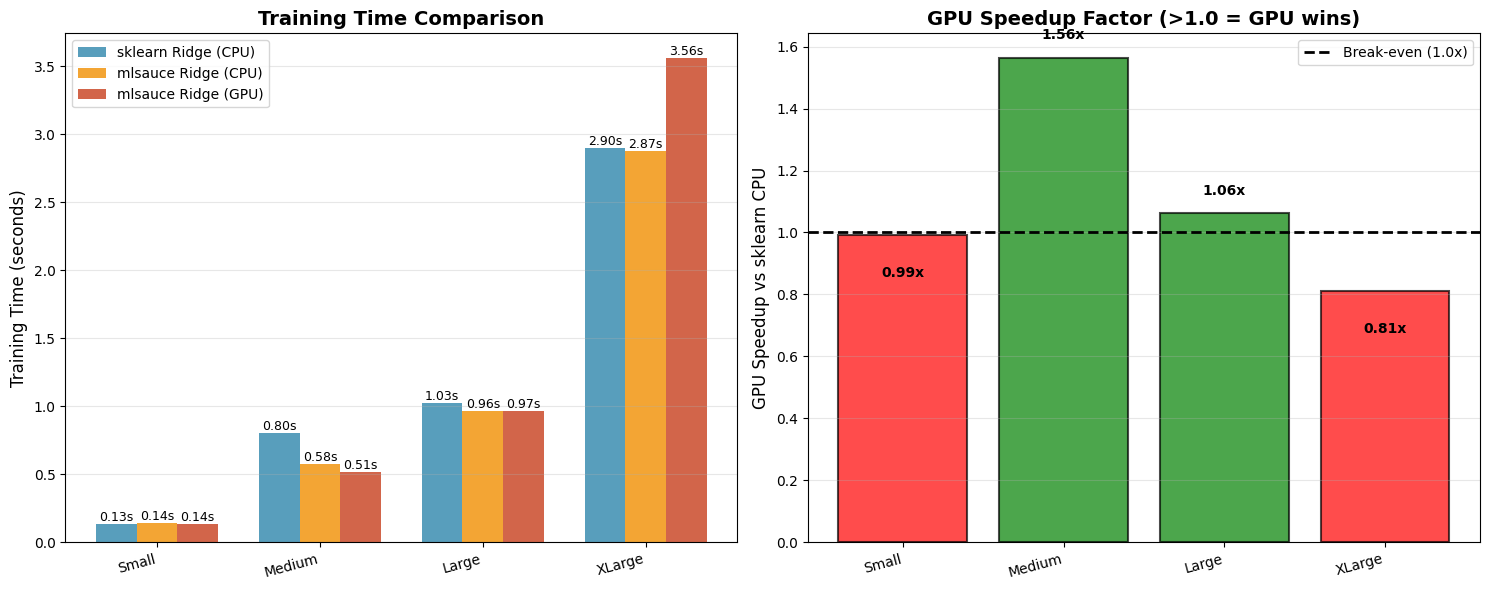
GPU also for CustomRegressor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from time import time
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
try:
from nnetsauce import CustomRegressor
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: nnetsauce is not installed.")
exit(1)
try:
import mlsauce as ms
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = True
except ImportError:
print("WARNING: mlsauce is not installed.")
MLSAUCE_AVAILABLE = False
exit(1)
print("="*80)
print("LARGE-SCALE GPU BENCHMARK")
print("Simulating the PDF example: 10,000 samples × 100 features")
print("="*80)
# Configuration matching the PDF's large-scale example
np.random.seed(42)
# Test different dataset sizes
dataset_configs = [
(1000, 50, "Small: 1K samples × 50 features"),
(5000, 100, "Medium: 5K samples × 100 features"),
(10000, 100, "Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example)"),
(20000, 150, "XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features"),
]
n_hidden = 100 # Fixed hidden features
results = {
'config': [],
'sklearn_cpu': [],
'mlsauce_cpu': [],
'mlsauce_gpu': [],
'gpu_speedup': [],
}
print("\nRunning benchmarks...\n")
for n_samples, n_features, description in dataset_configs:
print(f"\n{'='*80}")
print(f"{description}")
print(f"{'='*80}")
# Generate synthetic data
print(f"Generating {n_samples:,} samples with {n_features} features...")
X = np.random.randn(n_samples, n_features)
y = np.random.randn(n_samples)
# Split
split = int(0.8 * n_samples)
X_train, X_test = X[:split], X[split:]
y_train, y_test = y[:split], y[split:]
results['config'].append(description)
# 1. sklearn Ridge (CPU)
print("\n1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...")
start = time()
model_sklearn = CustomRegressor(
obj=Ridge(alpha=1.0),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
)
model_sklearn.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_sklearn.predict(X_test)
elapsed_sklearn = time() - start
results['sklearn_cpu'].append(elapsed_sklearn)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_sklearn:.3f}s")
# 2. mlsauce Ridge (CPU)
print("2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...")
start = time()
model_mlsauce_cpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="cpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
backend='cpu',
)
model_mlsauce_cpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_mlsauce_cpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_cpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_cpu'].append(elapsed_ml_cpu)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_ml_cpu:.3f}s")
print(f" Speedup vs sklearn: {elapsed_sklearn/elapsed_ml_cpu:.2f}x")
# 3. mlsauce Ridge (GPU)
print("3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...")
try:
start = time()
model_mlsauce_gpu = CustomRegressor(
obj=ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1.0, backend="gpu"),
n_hidden_features=n_hidden,
activation_name='relu',
nodes_sim='sobol',
backend='gpu'
)
model_mlsauce_gpu.fit(X_train, y_train)
_ = model_mlsauce_gpu.predict(X_test)
elapsed_ml_gpu = time() - start
results['mlsauce_gpu'].append(elapsed_ml_gpu)
speedup = elapsed_sklearn / elapsed_ml_gpu
results['gpu_speedup'].append(speedup)
print(f" Time: {elapsed_ml_gpu:.3f}s")
print(f" Speedup vs sklearn: {speedup:.2f}x")
print(f" Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: {elapsed_ml_cpu/elapsed_ml_gpu:.2f}x")
if speedup > 1.0:
print(f" ✓ GPU IS FASTER!")
else:
print(f" ✗ GPU overhead still dominates")
except Exception as e:
print(f" FAILED: {str(e)[:60]}...")
results['mlsauce_gpu'].append(None)
results['gpu_speedup'].append(None)
# Visualization
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 6))
# Plot 1: Absolute times
x_pos = np.arange(len(results['config']))
width = 0.25
ax1.bar(x_pos - width, results['sklearn_cpu'], width,
label='sklearn Ridge (CPU)', color='#2E86AB', alpha=0.8)
ax1.bar(x_pos, results['mlsauce_cpu'], width,
label='mlsauce Ridge (CPU)', color='#F18F01', alpha=0.8)
gpu_times = [t if t is not None else 0 for t in results['mlsauce_gpu']]
ax1.bar(x_pos + width, gpu_times, width,
label='mlsauce Ridge (GPU)', color='#C73E1D', alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_ylabel('Training Time (seconds)', fontsize=12)
ax1.set_title('Training Time Comparison', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax1.set_xticks(x_pos)
ax1.set_xticklabels([c.split(':')[0] for c in results['config']], rotation=15, ha='right')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# Add value labels on bars
for i, v in enumerate(results['sklearn_cpu']):
ax1.text(i - width, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
for i, v in enumerate(results['mlsauce_cpu']):
ax1.text(i, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
for i, v in enumerate(gpu_times):
if v > 0:
ax1.text(i + width, v, f'{v:.2f}s', ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=9)
# Plot 2: Speedup factors
valid_speedups = [s if s is not None else 0 for s in results['gpu_speedup']]
colors = ['green' if s > 1.0 else 'red' for s in valid_speedups]
bars = ax2.bar(x_pos, valid_speedups, color=colors, alpha=0.7, edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.5)
ax2.axhline(y=1.0, color='black', linestyle='--', linewidth=2, label='Break-even (1.0x)')
ax2.set_ylabel('GPU Speedup vs sklearn CPU', fontsize=12)
ax2.set_title('GPU Speedup Factor (>1.0 = GPU wins)', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
ax2.set_xticks(x_pos)
ax2.set_xticklabels([c.split(':')[0] for c in results['config']], rotation=15, ha='right')
ax2.grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
ax2.legend()
# Add value labels
for i, (bar, val) in enumerate(zip(bars, valid_speedups)):
if val > 0:
label = f'{val:.2f}x'
y_pos = val + 0.05 if val > 1.0 else val - 0.1
ax2.text(i, y_pos, label, ha='center', va='bottom' if val > 1.0 else 'top',
fontweight='bold', fontsize=10)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png', dpi=150, bbox_inches='tight')
print("\n\nSaved: large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png")
# Summary table
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("BENCHMARK SUMMARY")
print("="*100)
print(f"\n{'Configuration':<40} {'sklearn CPU':<12} {'mlsauce CPU':<12} {'mlsauce GPU':<12} {'GPU Speedup':<12}")
print("-"*100)
for i, config in enumerate(results['config']):
sk = results['sklearn_cpu'][i]
ml_cpu = results['mlsauce_cpu'][i]
ml_gpu = results['mlsauce_gpu'][i]
speedup = results['gpu_speedup'][i]
gpu_str = f"{ml_gpu:.3f}s" if ml_gpu else "N/A"
speedup_str = f"{speedup:.2f}x" if speedup else "N/A"
print(f"{config:<40} {sk:<12.3f}s {ml_cpu:<12.3f}s {gpu_str:<12} {speedup_str:<12}")
print("-"*100)
# Key insights
print("\n" + "="*100)
print("KEY INSIGHTS")
print("="*100)
gpu_wins = [i for i, s in enumerate(results['gpu_speedup']) if s and s > 1.0]
if gpu_wins:
print(f"\n✓ GPU becomes advantageous at:")
for i in gpu_wins:
speedup = results['gpu_speedup'][i]
print(f" - {results['config'][i]}: {speedup:.2f}x speedup")
else:
print("\n✗ GPU did not outperform CPU in any configuration tested")
print(" Reasons:")
print(" - GPU overhead (data transfer, compilation) > computation time")
print(" - Dataset still too small to amortize GPU setup costs")
print("\n💡 For GPU to be beneficial, you typically need:")
print(" 1. Dataset: 50,000+ samples (PDF showed 1M+ data points)")
print(" 2. Multiple iterations (cross-validation, hyperparameter tuning)")
print(" 3. Batch predictions (forecasting 100+ time series simultaneously)")
print(" 4. High-dimensional features (200+)")
print(" 5. Deep architectures (multiple hidden layers)")
print("\n" + "="*100)
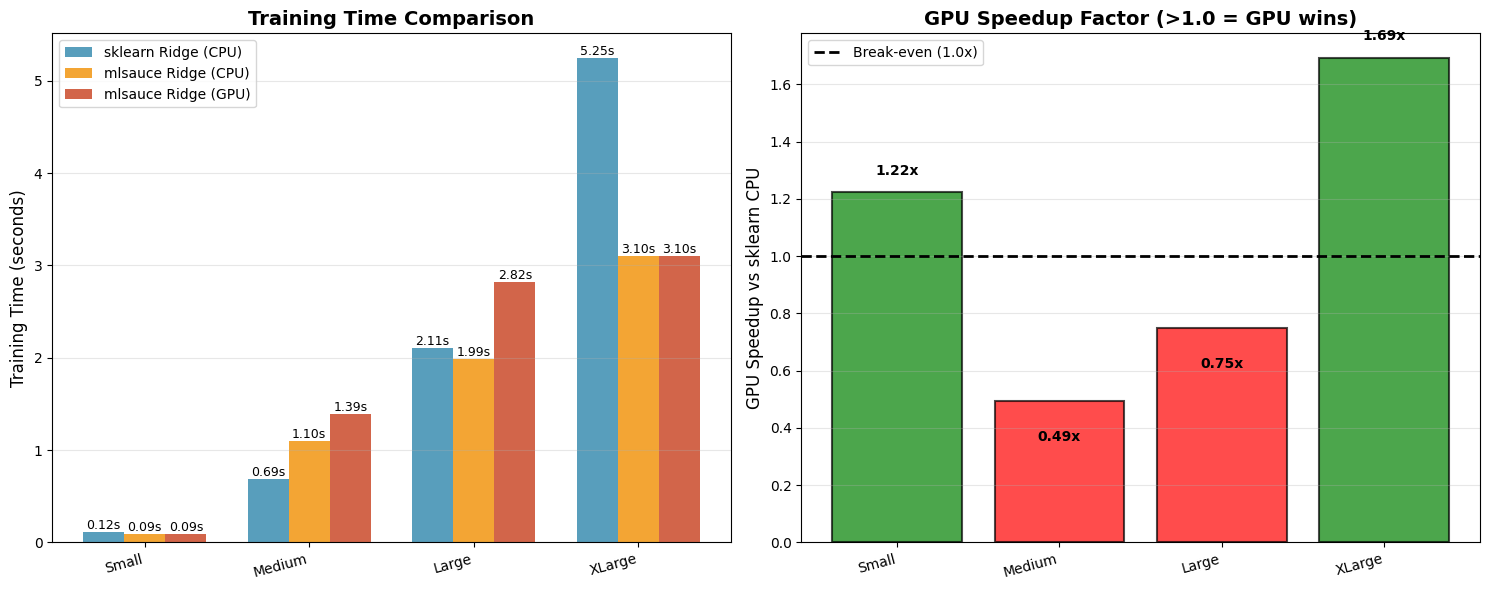
================================================================================
LARGE-SCALE GPU BENCHMARK
Simulating the PDF example: 10,000 samples × 100 features
================================================================================
Running benchmarks...
================================================================================
Small: 1K samples × 50 features
================================================================================
Generating 1,000 samples with 50 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.116s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.094s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.24x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 0.095s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.22x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 0.99x
✓ GPU IS FASTER!
================================================================================
Medium: 5K samples × 100 features
================================================================================
Generating 5,000 samples with 100 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 0.687s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 1.099s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.63x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 1.391s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.49x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 0.79x
✗ GPU overhead still dominates
================================================================================
Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example)
================================================================================
Generating 10,000 samples with 100 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 2.107s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 1.991s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.06x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 2.817s
Speedup vs sklearn: 0.75x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 0.71x
✗ GPU overhead still dominates
================================================================================
XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features
================================================================================
Generating 20,000 samples with 150 features...
1. Testing sklearn Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 5.251s
2. Testing mlsauce Ridge (CPU)...
Time: 3.100s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.69x
3. Testing mlsauce Ridge (GPU)...
Time: 3.101s
Speedup vs sklearn: 1.69x
Speedup vs mlsauce CPU: 1.00x
✓ GPU IS FASTER!
Saved: large_scale_gpu_benchmark.png
====================================================================================================
BENCHMARK SUMMARY
====================================================================================================
Configuration sklearn CPU mlsauce CPU mlsauce GPU GPU Speedup
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Small: 1K samples × 50 features 0.116 s 0.094 s 0.095s 1.22x
Medium: 5K samples × 100 features 0.687 s 1.099 s 1.391s 0.49x
Large: 10K samples × 100 features (PDF example) 2.107 s 1.991 s 2.817s 0.75x
XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features 5.251 s 3.100 s 3.101s 1.69x
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
====================================================================================================
KEY INSIGHTS
====================================================================================================
✓ GPU becomes advantageous at:
- Small: 1K samples × 50 features: 1.22x speedup
- XLarge: 20K samples × 150 features: 1.69x speedup
💡 For GPU to be beneficial, you typically need:
1. Dataset: 50,000+ samples (PDF showed 1M+ data points)
2. Multiple iterations (cross-validation, hyperparameter tuning)
3. Batch predictions (forecasting 100+ time series simultaneously)
4. High-dimensional features (200+)
5. Deep architectures (multiple hidden layers)
====================================================================================================
For attribution, please cite this work as:
T. Moudiki (2026-01-29). Overfitting and scaling (on GPU T4) tests on nnetsauce.CustomRegressor. Retrieved from https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2026/01/29/python/Overfitting-CustomRegressor
BibTeX citation (remove empty spaces)
@misc{ tmoudiki20260129,
author = { T. Moudiki },
title = { Overfitting and scaling (on GPU T4) tests on nnetsauce.CustomRegressor },
url = { https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2026/01/29/python/Overfitting-CustomRegressor },
year = { 2026 } }
Previous publications
- Explaining Time-Series Forecasts with Exact Shapley Values (ahead::dynrmf with external regressors applied to scenarios) Mar 8, 2026
- My Presentation at Risk 2026: Lightweight Transfer Learning for Financial Forecasting Mar 1, 2026
- nnetsauce with and without jax for GPU acceleration Feb 23, 2026
- Understanding Boosted Configuration Networks (combined neural networks and boosting): An Intuitive Guide Through Their Hyperparameters Feb 16, 2026
- R version of Python package survivalist, for model-agnostic survival analysis Feb 9, 2026
- Presenting Lightweight Transfer Learning for Financial Forecasting (Risk 2026) Feb 4, 2026
- Option pricing using time series models as market price of risk Feb 1, 2026
- Enhancing Time Series Forecasting (ahead::ridge2f) with Attention-Based Context Vectors (ahead::contextridge2f) Jan 31, 2026
- Overfitting and scaling (on GPU T4) tests on nnetsauce.CustomRegressor Jan 29, 2026
- Beyond Cross-validation: Hyperparameter Optimization via Generalization Gap Modeling Jan 25, 2026
- GPopt for Machine Learning (hyperparameters' tuning) Jan 21, 2026
- rtopy: an R to Python bridge -- novelties Jan 8, 2026
- Python examples for 'Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model- agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation' Jan 3, 2026
- Forecasting benchmark: Dynrmf (a new serious competitor in town) vs Theta Method on M-Competitions and Tourism competitition Jan 1, 2026
- Finally figured out a way to port python packages to R using uv and reticulate: example with nnetsauce Dec 17, 2025
- Overfitting Random Fourier Features: Universal Approximation Property Dec 13, 2025
- Counterfactual Scenario Analysis with ahead::ridge2f Dec 11, 2025
- Zero-Shot Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting with TabPFN 2.5 and nnetsauce Dec 10, 2025
- ARIMA Pricing: Semi-Parametric Market price of risk for Risk-Neutral Pricing (code + preprint) Dec 7, 2025
- Analyzing Paper Reviews with LLMs: I Used ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Qwen, Mistral, Gemini, and Claude (and you should too + publish the analysis) Dec 3, 2025
- tisthemachinelearner: New Workflow with uv for R Integration of scikit-learn Dec 1, 2025
- (ICYMI) RPweave: Unified R + Python + LaTeX System using uv Nov 21, 2025
- unifiedml: A Unified Machine Learning Interface for R, is now on CRAN + Discussion about AI replacing humans Nov 16, 2025
- Context-aware Theta forecasting Method: Extending Classical Time Series Forecasting with Machine Learning Nov 13, 2025
- unifiedml in R: A Unified Machine Learning Interface Nov 5, 2025
- Deterministic Shift Adjustment in Arbitrage-Free Pricing (historical to risk-neutral short rates) Oct 28, 2025
- New instantaneous short rates models with their deterministic shift adjustment, for historical and risk-neutral simulation Oct 27, 2025
- RPweave: Unified R + Python + LaTeX System using uv Oct 19, 2025
- GAN-like Synthetic Data Generation Examples (on univariate, multivariate distributions, digits recognition, Fashion-MNIST, stock returns, and Olivetti faces) with DistroSimulator Oct 19, 2025
- R port of llama2.c Oct 9, 2025
- Native uncertainty quantification for time series with NGBoost Oct 8, 2025
- NGBoost (Natural Gradient Boosting) for Regression, Classification, Time Series forecasting and Reserving Oct 6, 2025
- Real-time pricing with a pretrained probabilistic stock return model Oct 1, 2025
- Combining any model with GARCH(1,1) for probabilistic stock forecasting Sep 23, 2025
- Generating Synthetic Data with R-vine Copulas using esgtoolkit in R Sep 21, 2025
- Reimagining Equity Solvency Capital Requirement Approximation (one of my Master's Thesis subjects): From Bilinear Interpolation to Probabilistic Machine Learning Sep 16, 2025
- Transfer Learning using ahead::ridge2f on synthetic stocks returns Pt.2: synthetic data generation Sep 9, 2025
- Transfer Learning using ahead::ridge2f on synthetic stocks returns Sep 8, 2025
- I'm supposed to present 'Conformal Predictive Simulations for Univariate Time Series' at COPA CONFERENCE 2025 in London... Sep 4, 2025
- external regressors in ahead::dynrmf's interface for Machine learning forecasting Sep 1, 2025
- Another interesting decision, now for 'Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model-agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation' Aug 20, 2025
- Boosting any randomized based learner for regression, classification and univariate/multivariate time series forcasting Jul 26, 2025
- New nnetsauce version with CustomBackPropRegressor (CustomRegressor with Backpropagation) and ElasticNet2Regressor (Ridge2 with ElasticNet regularization) Jul 15, 2025
- mlsauce (home to a model-agnostic gradient boosting algorithm) can now be installed from PyPI. Jul 10, 2025
- A user-friendly graphical interface to techtonique dot net's API (will eventually contain graphics). Jul 8, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_MLCLASSIFICATION for Machine Learning supervised CLASSIFICATION in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 7, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_MLREGRESSION for Machine Learning supervised regression in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 6, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_RESERVING and =TECHTO_MLRESERVING for claims triangle reserving in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 5, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_SURVIVAL for Survival Analysis in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 4, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_SIMULATION for Stochastic Simulation in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 3, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_FORECAST for forecasting in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 2, 2025
- Random Vector Functional Link (RVFL) artificial neural network with 2 regularization parameters successfully used for forecasting/synthetic simulation in professional settings: Extensions (including Bayesian) Jul 1, 2025
- R version of 'Backpropagating quasi-randomized neural networks' Jun 24, 2025
- Backpropagating quasi-randomized neural networks Jun 23, 2025
- Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging any statistical model for volatility forecasting Jun 21, 2025
- Stacked generalization (Machine Learning model stacking) + conformal prediction for forecasting with ahead::mlf Jun 18, 2025
- An Overfitting dilemma: XGBoost Default Hyperparameters vs GenericBooster + LinearRegression Default Hyperparameters Jun 14, 2025
- Programming language-agnostic reserving using RidgeCV, LightGBM, XGBoost, and ExtraTrees Machine Learning models Jun 13, 2025
- Free R, Python and SQL editors in techtonique dot net Jun 9, 2025
- Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model-agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation Jun 7, 2025
- scikit-learn, glmnet, xgboost, lightgbm, pytorch, keras, nnetsauce in probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 6, 2025
- R version of Probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 5, 2025
- Probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 4, 2025
- Python version of Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging model-agnostic Quasi-Randomized networks and conformal prediction for nonparametric probabilistic stock forecasting (ML-ARCH) Jun 3, 2025
- Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging model-agnostic Machine Learning and conformal prediction for nonparametric probabilistic stock forecasting (ML-ARCH) Jun 2, 2025
- Permutations and SHAPley values for feature importance in techtonique dot net's API (with R + Python + the command line) Jun 1, 2025
- Which patient is going to survive longer? Another guide to using techtonique dot net's API (with R + Python + the command line) for survival analysis May 31, 2025
- A Guide to Using techtonique.net's API and rush for simulating and plotting Stochastic Scenarios May 30, 2025
- Simulating Stochastic Scenarios with Diffusion Models: A Guide to Using techtonique.net's API for the purpose May 29, 2025
- Will my apartment in 5th avenue be overpriced or not? Harnessing the power of www.techtonique.net (+ xgboost, lightgbm, catboost) to find out May 28, 2025
- How long must I wait until something happens: A Comprehensive Guide to Survival Analysis via an API May 27, 2025
- Harnessing the Power of techtonique.net: A Comprehensive Guide to Machine Learning Classification via an API May 26, 2025
- Quantile regression with any regressor -- Examples with RandomForestRegressor, RidgeCV, KNeighborsRegressor May 20, 2025
- Survival stacking: survival analysis translated as supervised classification in R and Python May 5, 2025
- 'Bayesian' optimization of hyperparameters in a R machine learning model using the bayesianrvfl package Apr 25, 2025
- A lightweight interface to scikit-learn in R: Bayesian and Conformal prediction Apr 21, 2025
- A lightweight interface to scikit-learn in R Pt.2: probabilistic time series forecasting in conjunction with ahead::dynrmf Apr 20, 2025
- Extending the Theta forecasting method to GLMs, GAMs, GLMBOOST and attention: benchmarking on Tourism, M1, M3 and M4 competition data sets (28000 series) Apr 14, 2025
- Extending the Theta forecasting method to GLMs and attention Apr 8, 2025
- Nonlinear conformalized Generalized Linear Models (GLMs) with R package 'rvfl' (and other models) Mar 31, 2025
- Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting (predictive simulations) in Microsoft Excel using Python, xlwings lite and www.techtonique.net Mar 28, 2025
- Conformalize (improved prediction intervals and simulations) any R Machine Learning model with misc::conformalize Mar 25, 2025
- My poster for the 18th FINANCIAL RISKS INTERNATIONAL FORUM by Institut Louis Bachelier/Fondation du Risque/Europlace Institute of Finance Mar 19, 2025
- Interpretable probabilistic kernel ridge regression using Matérn 3/2 kernels Mar 16, 2025
- (News from) Probabilistic Forecasting of univariate and multivariate Time Series using Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks (Ridge2) and Conformal Prediction Mar 9, 2025
- Word-Online: re-creating Karpathy's char-RNN (with supervised linear online learning of word embeddings) for text completion Mar 8, 2025
- CRAN-like repository for most recent releases of Techtonique's R packages Mar 2, 2025
- Presenting 'Online Probabilistic Estimation of Carbon Beta and Carbon Shapley Values for Financial and Climate Risk' at Institut Louis Bachelier Feb 27, 2025
- Web app with DeepSeek R1 and Hugging Face API for chatting Feb 23, 2025
- tisthemachinelearner: A Lightweight interface to scikit-learn with 2 classes, Classifier and Regressor (in Python and R) Feb 17, 2025
- R version of survivalist: Probabilistic model-agnostic survival analysis using scikit-learn, xgboost, lightgbm (and conformal prediction) Feb 12, 2025
- Model-agnostic global Survival Prediction of Patients with Myeloid Leukemia in QRT/Gustave Roussy Challenge (challengedata.ens.fr): Python's survivalist Quickstart Feb 10, 2025
- A simple test of the martingale hypothesis in esgtoolkit Feb 3, 2025
- Command Line Interface (CLI) for techtonique.net's API Jan 31, 2025
- Gradient-Boosting and Boostrap aggregating anything (alert: high performance): Part5, easier install and Rust backend Jan 27, 2025
- Just got a paper on conformal prediction REJECTED by International Journal of Forecasting despite evidence on 30,000 time series (and more). What's going on? Part2: 1311 time series from the Tourism competition Jan 20, 2025
- Techtonique is out! (with a tutorial in various programming languages and formats) Jan 14, 2025
- Univariate and Multivariate Probabilistic Forecasting with nnetsauce and TabPFN Jan 14, 2025
- Just got a paper on conformal prediction REJECTED by International Journal of Forecasting despite evidence on 30,000 time series (and more). What's going on? Jan 5, 2025
- Python and Interactive dashboard version of Stock price forecasting with Deep Learning: throwing power at the problem (and why it won't make you rich) Dec 31, 2024
- Stock price forecasting with Deep Learning: throwing power at the problem (and why it won't make you rich) Dec 29, 2024
- No-code Machine Learning Cross-validation and Interpretability in techtonique.net Dec 23, 2024
- survivalist: Probabilistic model-agnostic survival analysis using scikit-learn, glmnet, xgboost, lightgbm, pytorch, keras, nnetsauce and mlsauce Dec 15, 2024
- Model-agnostic 'Bayesian' optimization (for hyperparameter tuning) using conformalized surrogates in GPopt Dec 9, 2024
- You can beat Forecasting LLMs (Large Language Models a.k.a foundation models) with nnetsauce.MTS Pt.2: Generic Gradient Boosting Dec 1, 2024
- You can beat Forecasting LLMs (Large Language Models a.k.a foundation models) with nnetsauce.MTS Nov 24, 2024
- Unified interface and conformal prediction (calibrated prediction intervals) for R package forecast (and 'affiliates') Nov 23, 2024
- GLMNet in Python: Generalized Linear Models Nov 18, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part4, Time series forecasting Nov 10, 2024
- Predictive scenarios simulation in R, Python and Excel using Techtonique API Nov 3, 2024
- Chat with your tabular data in www.techtonique.net Oct 30, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part3, Histogram-based boosting Oct 28, 2024
- R editor and SQL console (in addition to Python editors) in www.techtonique.net Oct 21, 2024
- R and Python consoles + JupyterLite in www.techtonique.net Oct 15, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part2, R version Oct 14, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance) Oct 6, 2024
- Benchmarking 30 statistical/Machine Learning models on the VN1 Forecasting -- Accuracy challenge Oct 4, 2024
- Automated random variable distribution inference using Kullback-Leibler divergence and simulating best-fitting distribution Oct 2, 2024
- Forecasting in Excel using Techtonique's Machine Learning APIs under the hood Sep 30, 2024
- Techtonique web app for data-driven decisions using Mathematics, Statistics, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization Sep 25, 2024
- Parallel for loops (Map or Reduce) + New versions of nnetsauce and ahead Sep 16, 2024
- Adaptive (online/streaming) learning with uncertainty quantification using Polyak averaging in learningmachine Sep 10, 2024
- New versions of nnetsauce and ahead Sep 9, 2024
- Prediction sets and prediction intervals for conformalized Auto XGBoost, Auto LightGBM, Auto CatBoost, Auto GradientBoosting Sep 2, 2024
- Quick/automated R package development workflow (assuming you're using macOS or Linux) Part2 Aug 30, 2024
- R package development workflow (assuming you're using macOS or Linux) Aug 27, 2024
- A new method for deriving a nonparametric confidence interval for the mean Aug 26, 2024
- Conformalized adaptive (online/streaming) learning using learningmachine in Python and R Aug 19, 2024
- Bayesian (nonlinear) adaptive learning Aug 12, 2024
- Auto XGBoost, Auto LightGBM, Auto CatBoost, Auto GradientBoosting Aug 5, 2024
- Copulas for uncertainty quantification in time series forecasting Jul 28, 2024
- Forecasting uncertainty: sequential split conformal prediction + Block bootstrap (web app) Jul 22, 2024
- learningmachine for Python (new version) Jul 15, 2024
- learningmachine v2.0.0: Machine Learning with explanations and uncertainty quantification Jul 8, 2024
- My presentation at ISF 2024 conference (slides with nnetsauce probabilistic forecasting news) Jul 3, 2024
- 10 uncertainty quantification methods in nnetsauce forecasting Jul 1, 2024
- Forecasting with XGBoost embedded in Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks Jun 24, 2024
- Forecasting Monthly Airline Passenger Numbers with Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks Jun 17, 2024
- Automated hyperparameter tuning using any conformalized surrogate Jun 9, 2024
- Recognizing handwritten digits with Ridge2Classifier Jun 3, 2024
- Forecasting the Economy May 27, 2024
- A detailed introduction to Deep Quasi-Randomized 'neural' networks May 19, 2024
- Probability of receiving a loan; using learningmachine May 12, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.18.2`: various examples and benchmarks with dimension reduction May 6, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.17.0`: boosting with Elastic Net, polynomials and heterogeneity in explanatory variables Apr 29, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.13.0`: taking into account inputs heterogeneity through clustering Apr 21, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.12.0`: prediction intervals for LSBoostRegressor Apr 15, 2024
- Conformalized predictive simulations for univariate time series on more than 250 data sets Apr 7, 2024
- learningmachine v1.1.2: for Python Apr 1, 2024
- learningmachine v1.0.0: prediction intervals around the probability of the event 'a tumor being malignant' Mar 25, 2024
- Bayesian inference and conformal prediction (prediction intervals) in nnetsauce v0.18.1 Mar 18, 2024
- Multiple examples of Machine Learning forecasting with ahead Mar 11, 2024
- rtopy (v0.1.1): calling R functions in Python Mar 4, 2024
- ahead forecasting (v0.10.0): fast time series model calibration and Python plots Feb 26, 2024
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Part3: how many times do couples cheat on each other? Feb 19, 2024
- nnetsauce's introduction as of 2024-02-11 (new version 0.17.0) Feb 11, 2024
- Tuning Machine Learning models with GPopt's new version Part 2 Feb 5, 2024
- Tuning Machine Learning models with GPopt's new version Jan 29, 2024
- Subsampling continuous and discrete response variables Jan 22, 2024
- DeepMTS, a Deep Learning Model for Multivariate Time Series Jan 15, 2024
- A classifier that's very accurate (and deep) Pt.2: there are > 90 classifiers in nnetsauce Jan 8, 2024
- learningmachine: prediction intervals for conformalized Kernel ridge regression and Random Forest Jan 1, 2024
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Part2: how many times do couples cheat on each other? Descriptive analytics, interpretability and prediction intervals using conformal prediction Dec 25, 2023
- Diffusion models in Python with esgtoolkit (Part2) Dec 18, 2023
- Diffusion models in Python with esgtoolkit Dec 11, 2023
- Julia packaging at the command line Dec 4, 2023
- Quasi-randomized nnetworks in Julia, Python and R Nov 27, 2023
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Nov 20, 2023
- A classifier that's very accurate (and deep) Nov 12, 2023
- mlsauce version 0.8.10: Statistical/Machine Learning with Python and R Nov 5, 2023
- AutoML in nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized nnetworks) Pt.2: multivariate time series forecasting Oct 29, 2023
- AutoML in nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized nnetworks) Oct 22, 2023
- Version v0.14.0 of nnetsauce for R and Python Oct 16, 2023
- A diffusion model: G2++ Oct 9, 2023
- Diffusion models in ESGtoolkit + announcements Oct 2, 2023
- An infinity of time series forecasting models in nnetsauce (Part 2 with uncertainty quantification) Sep 25, 2023
- (News from) forecasting in Python with ahead (progress bars and plots) Sep 18, 2023
- Forecasting in Python with ahead Sep 11, 2023
- Risk-neutralize simulations Sep 4, 2023
- Comparing cross-validation results using crossval_ml and boxplots Aug 27, 2023
- Reminder Apr 30, 2023
- Did you ask ChatGPT about who you are? Apr 16, 2023
- A new version of nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized 'neural' networks) Apr 2, 2023
- Simple interfaces to the forecasting API Nov 23, 2022
- A web application for forecasting in Python, R, Ruby, C#, JavaScript, PHP, Go, Rust, Java, MATLAB, etc. Nov 2, 2022
- Prediction intervals (not only) for Boosted Configuration Networks in Python Oct 5, 2022
- Boosted Configuration (neural) Networks Pt. 2 Sep 3, 2022
- Boosted Configuration (_neural_) Networks for classification Jul 21, 2022
- A Machine Learning workflow using Techtonique Jun 6, 2022
- Super Mario Bros © in the browser using PyScript May 8, 2022
- News from ESGtoolkit, ycinterextra, and nnetsauce Apr 4, 2022
- Explaining a Keras _neural_ network predictions with the-teller Mar 11, 2022
- New version of nnetsauce -- various quasi-randomized networks Feb 12, 2022
- A dashboard illustrating bivariate time series forecasting with `ahead` Jan 14, 2022
- Hundreds of Statistical/Machine Learning models for univariate time series, using ahead, ranger, xgboost, and caret Dec 20, 2021
- Forecasting with `ahead` (Python version) Dec 13, 2021
- Tuning and interpreting LSBoost Nov 15, 2021
- Time series cross-validation using `crossvalidation` (Part 2) Nov 7, 2021
- Fast and scalable forecasting with ahead::ridge2f Oct 31, 2021
- Automatic Forecasting with `ahead::dynrmf` and Ridge regression Oct 22, 2021
- Forecasting with `ahead` Oct 15, 2021
- Classification using linear regression Sep 26, 2021
- `crossvalidation` and random search for calibrating support vector machines Aug 6, 2021
- parallel grid search cross-validation using `crossvalidation` Jul 31, 2021
- `crossvalidation` on R-universe, plus a classification example Jul 23, 2021
- Documentation and source code for GPopt, a package for Bayesian optimization Jul 2, 2021
- Hyperparameters tuning with GPopt Jun 11, 2021
- A forecasting tool (API) with examples in curl, R, Python May 28, 2021
- Bayesian Optimization with GPopt Part 2 (save and resume) Apr 30, 2021
- Bayesian Optimization with GPopt Apr 16, 2021
- Compatibility of nnetsauce and mlsauce with scikit-learn Mar 26, 2021
- Explaining xgboost predictions with the teller Mar 12, 2021
- An infinity of time series models in nnetsauce Mar 6, 2021
- New activation functions in mlsauce's LSBoost Feb 12, 2021
- 2020 recap, Gradient Boosting, Generalized Linear Models, AdaOpt with nnetsauce and mlsauce Dec 29, 2020
- A deeper learning architecture in nnetsauce Dec 18, 2020
- Classify penguins with nnetsauce's MultitaskClassifier Dec 11, 2020
- Bayesian forecasting for uni/multivariate time series Dec 4, 2020
- Generalized nonlinear models in nnetsauce Nov 28, 2020
- Boosting nonlinear penalized least squares Nov 21, 2020
- Statistical/Machine Learning explainability using Kernel Ridge Regression surrogates Nov 6, 2020
- NEWS Oct 30, 2020
- A glimpse into my PhD journey Oct 23, 2020
- Submitting R package to CRAN Oct 16, 2020
- Simulation of dependent variables in ESGtoolkit Oct 9, 2020
- Forecasting lung disease progression Oct 2, 2020
- New nnetsauce Sep 25, 2020
- Technical documentation Sep 18, 2020
- A new version of nnetsauce, and a new Techtonique website Sep 11, 2020
- Back next week, and a few announcements Sep 4, 2020
- Explainable 'AI' using Gradient Boosted randomized networks Pt2 (the Lasso) Jul 31, 2020
- LSBoost: Explainable 'AI' using Gradient Boosted randomized networks (with examples in R and Python) Jul 24, 2020
- nnetsauce version 0.5.0, randomized neural networks on GPU Jul 17, 2020
- Maximizing your tip as a waiter (Part 2) Jul 10, 2020
- New version of mlsauce, with Gradient Boosted randomized networks and stump decision trees Jul 3, 2020
- Announcements Jun 26, 2020
- Parallel AdaOpt classification Jun 19, 2020
- Comments section and other news Jun 12, 2020
- Maximizing your tip as a waiter Jun 5, 2020
- AdaOpt classification on MNIST handwritten digits (without preprocessing) May 29, 2020
- AdaOpt (a probabilistic classifier based on a mix of multivariable optimization and nearest neighbors) for R May 22, 2020
- AdaOpt May 15, 2020
- Custom errors for cross-validation using crossval::crossval_ml May 8, 2020
- Documentation+Pypi for the `teller`, a model-agnostic tool for Machine Learning explainability May 1, 2020
- Encoding your categorical variables based on the response variable and correlations Apr 24, 2020
- Linear model, xgboost and randomForest cross-validation using crossval::crossval_ml Apr 17, 2020
- Grid search cross-validation using crossval Apr 10, 2020
- Documentation for the querier, a query language for Data Frames Apr 3, 2020
- Time series cross-validation using crossval Mar 27, 2020
- On model specification, identification, degrees of freedom and regularization Mar 20, 2020
- Import data into the querier (now on Pypi), a query language for Data Frames Mar 13, 2020
- R notebooks for nnetsauce Mar 6, 2020
- Version 0.4.0 of nnetsauce, with fruits and breast cancer classification Feb 28, 2020
- Create a specific feed in your Jekyll blog Feb 21, 2020
- Git/Github for contributing to package development Feb 14, 2020
- Feedback forms for contributing Feb 7, 2020
- nnetsauce for R Jan 31, 2020
- A new version of nnetsauce (v0.3.1) Jan 24, 2020
- ESGtoolkit, a tool for Monte Carlo simulation (v0.2.0) Jan 17, 2020
- Search bar, new year 2020 Jan 10, 2020
- 2019 Recap, the nnetsauce, the teller and the querier Dec 20, 2019
- Understanding model interactions with the `teller` Dec 13, 2019
- Using the `teller` on a classifier Dec 6, 2019
- Benchmarking the querier's verbs Nov 29, 2019
- Composing the querier's verbs for data wrangling Nov 22, 2019
- Comparing and explaining model predictions with the teller Nov 15, 2019
- Tests for the significance of marginal effects in the teller Nov 8, 2019
- Introducing the teller Nov 1, 2019
- Introducing the querier Oct 25, 2019
- Prediction intervals for nnetsauce models Oct 18, 2019
- Using R in Python for statistical learning/data science Oct 11, 2019
- Model calibration with `crossval` Oct 4, 2019
- Bagging in the nnetsauce Sep 25, 2019
- Adaboost learning with nnetsauce Sep 18, 2019
- Change in blog's presentation Sep 4, 2019
- nnetsauce on Pypi Jun 5, 2019
- More nnetsauce (examples of use) May 9, 2019
- nnetsauce Mar 13, 2019
- crossval Mar 13, 2019
- test Mar 10, 2019

Comments powered by Talkyard.