Today, give a try to Techtonique web app, a tool designed to help you make informed, data-driven decisions using Mathematics, Statistics, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization. Here is a tutorial with audio, video, code, and slides: https://moudiki2.gumroad.com/l/nrhgb. 100 API requests are now (and forever) offered to every user every month, no matter the pricing tier.
In a previous blog post,
I presented time series cross-validation with crossvalidation::crossval_ts. The most
recent version of package crossvalidation, v0.4.1, contains a new function called eval_ts.
How does crossvalidation::eval_ts work? As described in the graph below:
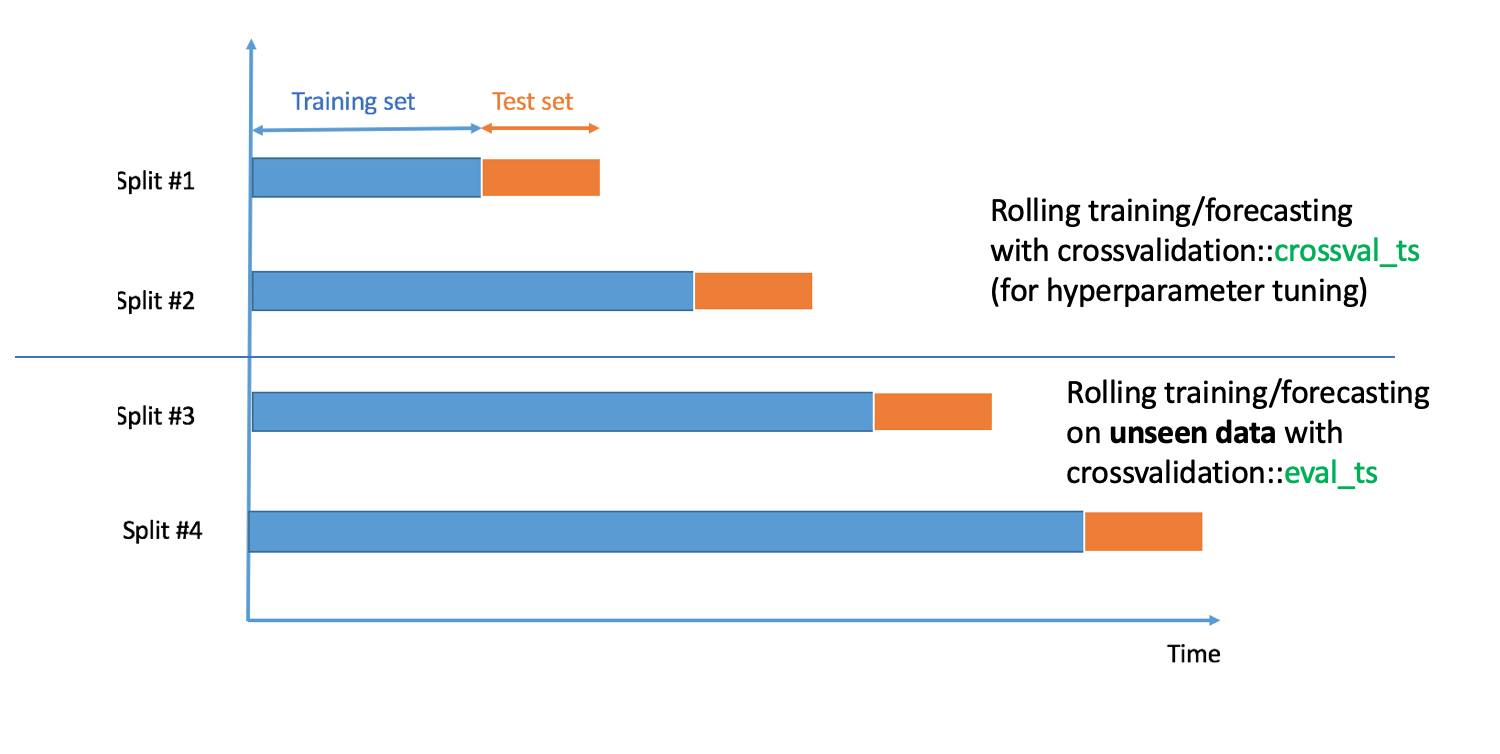
crossvalidation::crossval_ts and crossvalidation::eval_ts
have the same arguments, except,
an argument p for crossval_ts and an argument q for eval_ts. p is the percentage of original
data used for cross-validation and hyperparameter tuning, and q is the percentage of unseen data used
for model validation. In addition, and most importantly, we must have p + q = 1, to avoid overlapping
train/test/validation sets.
Here’s a concrete example of use of crossvalidation::eval_ts :
Installing packages
options(repos = c(
techtonique = 'https://techtonique.r-universe.dev',
CRAN = 'https://cloud.r-project.org'))
install.packages("ahead")
install.packages("crossvalidation")
install.packages("e1071")
Loading packages
library(ahead) # forecasting tool
library(crossvalidation) # cross-validation and evaluation
library(datasets) # dataset Nile
library(e1071) # for svm
Input data
y <- AirPassengers
Forecasting function
fcast_func <- function(y, h = 5, kernel=c("linear", "radial"))
{
kernel <- match.arg(kernel)
ahead::dynrmf(y=y, h=h, level=95,
fit_func = e1071::svm,
fit_params = list(kernel = kernel),
predict_func = predict)
}
We’ll consider that the hyperparameter is kernel, which is either “linear” or “radial”.
Error metric (Root Mean Squared Error, RMSE)
eval_metric <- function(predicted, observed)
{
return(sqrt(mean((observed - predicted) ^ 2, na.rm = FALSE)))
}
Cross-validation on 80% of the data
With kernel = "radial"
res_cv_radial <- crossvalidation::crossval_ts(y = y,
fcast_func = fcast_func,
fit_params = list(kernel = "radial"),
initial_window = 20,
horizon = 10, p=0.8,
eval_metric = eval_metric,
show_progress = FALSE)
print(median(res_cv_radial))
[1] 47.29141
With kernel = "linear"
res_cv_linear <- crossvalidation::crossval_ts(y = y,
fcast_func = fcast_func,
fit_params = list(kernel = "linear"),
initial_window = 20,
horizon = 10, p=0.8,
eval_metric = eval_metric,
show_progress = FALSE)
print(median(res_cv_linear))
[1] 44.18955
Evaluation with the **best hyperparameter, kernel = "linear", on unseen data (q = 1 - p) **
res_eval_linear <- crossvalidation::eval_ts(y = y,
fcast_func = fcast_func,
fit_params = list(kernel = "linear"),
initial_window = 20,
horizon = 10, q=0.2,
eval_metric = eval_metric,
show_progress = FALSE)
print(median(res_eval_linear))
[1] 86.47903
For attribution, please cite this work as:
T. Moudiki (2021-11-07). Time series cross-validation using `crossvalidation` (Part 2). Retrieved from https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2021/11/07/r/misc/timeseries/crossvalidation-eval-ts
BibTeX citation (remove empty spaces)
@misc{ tmoudiki20211107,
author = { T. Moudiki },
title = { Time series cross-validation using `crossvalidation` (Part 2) },
url = { https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2021/11/07/r/misc/timeseries/crossvalidation-eval-ts },
year = { 2021 } }
Previous publications
- Explaining Time-Series Forecasts with Exact Shapley Values (ahead::dynrmf with external regressors applied to scenarios) Mar 8, 2026
- My Presentation at Risk 2026: Lightweight Transfer Learning for Financial Forecasting Mar 1, 2026
- nnetsauce with and without jax for GPU acceleration Feb 23, 2026
- Understanding Boosted Configuration Networks (combined neural networks and boosting): An Intuitive Guide Through Their Hyperparameters Feb 16, 2026
- R version of Python package survivalist, for model-agnostic survival analysis Feb 9, 2026
- Presenting Lightweight Transfer Learning for Financial Forecasting (Risk 2026) Feb 4, 2026
- Option pricing using time series models as market price of risk Feb 1, 2026
- Enhancing Time Series Forecasting (ahead::ridge2f) with Attention-Based Context Vectors (ahead::contextridge2f) Jan 31, 2026
- Overfitting and scaling (on GPU T4) tests on nnetsauce.CustomRegressor Jan 29, 2026
- Beyond Cross-validation: Hyperparameter Optimization via Generalization Gap Modeling Jan 25, 2026
- GPopt for Machine Learning (hyperparameters' tuning) Jan 21, 2026
- rtopy: an R to Python bridge -- novelties Jan 8, 2026
- Python examples for 'Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model- agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation' Jan 3, 2026
- Forecasting benchmark: Dynrmf (a new serious competitor in town) vs Theta Method on M-Competitions and Tourism competitition Jan 1, 2026
- Finally figured out a way to port python packages to R using uv and reticulate: example with nnetsauce Dec 17, 2025
- Overfitting Random Fourier Features: Universal Approximation Property Dec 13, 2025
- Counterfactual Scenario Analysis with ahead::ridge2f Dec 11, 2025
- Zero-Shot Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting with TabPFN 2.5 and nnetsauce Dec 10, 2025
- ARIMA Pricing: Semi-Parametric Market price of risk for Risk-Neutral Pricing (code + preprint) Dec 7, 2025
- Analyzing Paper Reviews with LLMs: I Used ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Qwen, Mistral, Gemini, and Claude (and you should too + publish the analysis) Dec 3, 2025
- tisthemachinelearner: New Workflow with uv for R Integration of scikit-learn Dec 1, 2025
- (ICYMI) RPweave: Unified R + Python + LaTeX System using uv Nov 21, 2025
- unifiedml: A Unified Machine Learning Interface for R, is now on CRAN + Discussion about AI replacing humans Nov 16, 2025
- Context-aware Theta forecasting Method: Extending Classical Time Series Forecasting with Machine Learning Nov 13, 2025
- unifiedml in R: A Unified Machine Learning Interface Nov 5, 2025
- Deterministic Shift Adjustment in Arbitrage-Free Pricing (historical to risk-neutral short rates) Oct 28, 2025
- New instantaneous short rates models with their deterministic shift adjustment, for historical and risk-neutral simulation Oct 27, 2025
- RPweave: Unified R + Python + LaTeX System using uv Oct 19, 2025
- GAN-like Synthetic Data Generation Examples (on univariate, multivariate distributions, digits recognition, Fashion-MNIST, stock returns, and Olivetti faces) with DistroSimulator Oct 19, 2025
- R port of llama2.c Oct 9, 2025
- Native uncertainty quantification for time series with NGBoost Oct 8, 2025
- NGBoost (Natural Gradient Boosting) for Regression, Classification, Time Series forecasting and Reserving Oct 6, 2025
- Real-time pricing with a pretrained probabilistic stock return model Oct 1, 2025
- Combining any model with GARCH(1,1) for probabilistic stock forecasting Sep 23, 2025
- Generating Synthetic Data with R-vine Copulas using esgtoolkit in R Sep 21, 2025
- Reimagining Equity Solvency Capital Requirement Approximation (one of my Master's Thesis subjects): From Bilinear Interpolation to Probabilistic Machine Learning Sep 16, 2025
- Transfer Learning using ahead::ridge2f on synthetic stocks returns Pt.2: synthetic data generation Sep 9, 2025
- Transfer Learning using ahead::ridge2f on synthetic stocks returns Sep 8, 2025
- I'm supposed to present 'Conformal Predictive Simulations for Univariate Time Series' at COPA CONFERENCE 2025 in London... Sep 4, 2025
- external regressors in ahead::dynrmf's interface for Machine learning forecasting Sep 1, 2025
- Another interesting decision, now for 'Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model-agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation' Aug 20, 2025
- Boosting any randomized based learner for regression, classification and univariate/multivariate time series forcasting Jul 26, 2025
- New nnetsauce version with CustomBackPropRegressor (CustomRegressor with Backpropagation) and ElasticNet2Regressor (Ridge2 with ElasticNet regularization) Jul 15, 2025
- mlsauce (home to a model-agnostic gradient boosting algorithm) can now be installed from PyPI. Jul 10, 2025
- A user-friendly graphical interface to techtonique dot net's API (will eventually contain graphics). Jul 8, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_MLCLASSIFICATION for Machine Learning supervised CLASSIFICATION in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 7, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_MLREGRESSION for Machine Learning supervised regression in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 6, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_RESERVING and =TECHTO_MLRESERVING for claims triangle reserving in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 5, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_SURVIVAL for Survival Analysis in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 4, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_SIMULATION for Stochastic Simulation in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 3, 2025
- Calling =TECHTO_FORECAST for forecasting in Excel is just a matter of copying and pasting Jul 2, 2025
- Random Vector Functional Link (RVFL) artificial neural network with 2 regularization parameters successfully used for forecasting/synthetic simulation in professional settings: Extensions (including Bayesian) Jul 1, 2025
- R version of 'Backpropagating quasi-randomized neural networks' Jun 24, 2025
- Backpropagating quasi-randomized neural networks Jun 23, 2025
- Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging any statistical model for volatility forecasting Jun 21, 2025
- Stacked generalization (Machine Learning model stacking) + conformal prediction for forecasting with ahead::mlf Jun 18, 2025
- An Overfitting dilemma: XGBoost Default Hyperparameters vs GenericBooster + LinearRegression Default Hyperparameters Jun 14, 2025
- Programming language-agnostic reserving using RidgeCV, LightGBM, XGBoost, and ExtraTrees Machine Learning models Jun 13, 2025
- Free R, Python and SQL editors in techtonique dot net Jun 9, 2025
- Beyond Nelson-Siegel and splines: A model-agnostic Machine Learning framework for discount curve calibration, interpolation and extrapolation Jun 7, 2025
- scikit-learn, glmnet, xgboost, lightgbm, pytorch, keras, nnetsauce in probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 6, 2025
- R version of Probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 5, 2025
- Probabilistic Machine Learning (for longitudinal data) Reserving (work in progress) Jun 4, 2025
- Python version of Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging model-agnostic Quasi-Randomized networks and conformal prediction for nonparametric probabilistic stock forecasting (ML-ARCH) Jun 3, 2025
- Beyond ARMA-GARCH: leveraging model-agnostic Machine Learning and conformal prediction for nonparametric probabilistic stock forecasting (ML-ARCH) Jun 2, 2025
- Permutations and SHAPley values for feature importance in techtonique dot net's API (with R + Python + the command line) Jun 1, 2025
- Which patient is going to survive longer? Another guide to using techtonique dot net's API (with R + Python + the command line) for survival analysis May 31, 2025
- A Guide to Using techtonique.net's API and rush for simulating and plotting Stochastic Scenarios May 30, 2025
- Simulating Stochastic Scenarios with Diffusion Models: A Guide to Using techtonique.net's API for the purpose May 29, 2025
- Will my apartment in 5th avenue be overpriced or not? Harnessing the power of www.techtonique.net (+ xgboost, lightgbm, catboost) to find out May 28, 2025
- How long must I wait until something happens: A Comprehensive Guide to Survival Analysis via an API May 27, 2025
- Harnessing the Power of techtonique.net: A Comprehensive Guide to Machine Learning Classification via an API May 26, 2025
- Quantile regression with any regressor -- Examples with RandomForestRegressor, RidgeCV, KNeighborsRegressor May 20, 2025
- Survival stacking: survival analysis translated as supervised classification in R and Python May 5, 2025
- 'Bayesian' optimization of hyperparameters in a R machine learning model using the bayesianrvfl package Apr 25, 2025
- A lightweight interface to scikit-learn in R: Bayesian and Conformal prediction Apr 21, 2025
- A lightweight interface to scikit-learn in R Pt.2: probabilistic time series forecasting in conjunction with ahead::dynrmf Apr 20, 2025
- Extending the Theta forecasting method to GLMs, GAMs, GLMBOOST and attention: benchmarking on Tourism, M1, M3 and M4 competition data sets (28000 series) Apr 14, 2025
- Extending the Theta forecasting method to GLMs and attention Apr 8, 2025
- Nonlinear conformalized Generalized Linear Models (GLMs) with R package 'rvfl' (and other models) Mar 31, 2025
- Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting (predictive simulations) in Microsoft Excel using Python, xlwings lite and www.techtonique.net Mar 28, 2025
- Conformalize (improved prediction intervals and simulations) any R Machine Learning model with misc::conformalize Mar 25, 2025
- My poster for the 18th FINANCIAL RISKS INTERNATIONAL FORUM by Institut Louis Bachelier/Fondation du Risque/Europlace Institute of Finance Mar 19, 2025
- Interpretable probabilistic kernel ridge regression using Matérn 3/2 kernels Mar 16, 2025
- (News from) Probabilistic Forecasting of univariate and multivariate Time Series using Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks (Ridge2) and Conformal Prediction Mar 9, 2025
- Word-Online: re-creating Karpathy's char-RNN (with supervised linear online learning of word embeddings) for text completion Mar 8, 2025
- CRAN-like repository for most recent releases of Techtonique's R packages Mar 2, 2025
- Presenting 'Online Probabilistic Estimation of Carbon Beta and Carbon Shapley Values for Financial and Climate Risk' at Institut Louis Bachelier Feb 27, 2025
- Web app with DeepSeek R1 and Hugging Face API for chatting Feb 23, 2025
- tisthemachinelearner: A Lightweight interface to scikit-learn with 2 classes, Classifier and Regressor (in Python and R) Feb 17, 2025
- R version of survivalist: Probabilistic model-agnostic survival analysis using scikit-learn, xgboost, lightgbm (and conformal prediction) Feb 12, 2025
- Model-agnostic global Survival Prediction of Patients with Myeloid Leukemia in QRT/Gustave Roussy Challenge (challengedata.ens.fr): Python's survivalist Quickstart Feb 10, 2025
- A simple test of the martingale hypothesis in esgtoolkit Feb 3, 2025
- Command Line Interface (CLI) for techtonique.net's API Jan 31, 2025
- Gradient-Boosting and Boostrap aggregating anything (alert: high performance): Part5, easier install and Rust backend Jan 27, 2025
- Just got a paper on conformal prediction REJECTED by International Journal of Forecasting despite evidence on 30,000 time series (and more). What's going on? Part2: 1311 time series from the Tourism competition Jan 20, 2025
- Techtonique is out! (with a tutorial in various programming languages and formats) Jan 14, 2025
- Univariate and Multivariate Probabilistic Forecasting with nnetsauce and TabPFN Jan 14, 2025
- Just got a paper on conformal prediction REJECTED by International Journal of Forecasting despite evidence on 30,000 time series (and more). What's going on? Jan 5, 2025
- Python and Interactive dashboard version of Stock price forecasting with Deep Learning: throwing power at the problem (and why it won't make you rich) Dec 31, 2024
- Stock price forecasting with Deep Learning: throwing power at the problem (and why it won't make you rich) Dec 29, 2024
- No-code Machine Learning Cross-validation and Interpretability in techtonique.net Dec 23, 2024
- survivalist: Probabilistic model-agnostic survival analysis using scikit-learn, glmnet, xgboost, lightgbm, pytorch, keras, nnetsauce and mlsauce Dec 15, 2024
- Model-agnostic 'Bayesian' optimization (for hyperparameter tuning) using conformalized surrogates in GPopt Dec 9, 2024
- You can beat Forecasting LLMs (Large Language Models a.k.a foundation models) with nnetsauce.MTS Pt.2: Generic Gradient Boosting Dec 1, 2024
- You can beat Forecasting LLMs (Large Language Models a.k.a foundation models) with nnetsauce.MTS Nov 24, 2024
- Unified interface and conformal prediction (calibrated prediction intervals) for R package forecast (and 'affiliates') Nov 23, 2024
- GLMNet in Python: Generalized Linear Models Nov 18, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part4, Time series forecasting Nov 10, 2024
- Predictive scenarios simulation in R, Python and Excel using Techtonique API Nov 3, 2024
- Chat with your tabular data in www.techtonique.net Oct 30, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part3, Histogram-based boosting Oct 28, 2024
- R editor and SQL console (in addition to Python editors) in www.techtonique.net Oct 21, 2024
- R and Python consoles + JupyterLite in www.techtonique.net Oct 15, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance): Part2, R version Oct 14, 2024
- Gradient-Boosting anything (alert: high performance) Oct 6, 2024
- Benchmarking 30 statistical/Machine Learning models on the VN1 Forecasting -- Accuracy challenge Oct 4, 2024
- Automated random variable distribution inference using Kullback-Leibler divergence and simulating best-fitting distribution Oct 2, 2024
- Forecasting in Excel using Techtonique's Machine Learning APIs under the hood Sep 30, 2024
- Techtonique web app for data-driven decisions using Mathematics, Statistics, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization Sep 25, 2024
- Parallel for loops (Map or Reduce) + New versions of nnetsauce and ahead Sep 16, 2024
- Adaptive (online/streaming) learning with uncertainty quantification using Polyak averaging in learningmachine Sep 10, 2024
- New versions of nnetsauce and ahead Sep 9, 2024
- Prediction sets and prediction intervals for conformalized Auto XGBoost, Auto LightGBM, Auto CatBoost, Auto GradientBoosting Sep 2, 2024
- Quick/automated R package development workflow (assuming you're using macOS or Linux) Part2 Aug 30, 2024
- R package development workflow (assuming you're using macOS or Linux) Aug 27, 2024
- A new method for deriving a nonparametric confidence interval for the mean Aug 26, 2024
- Conformalized adaptive (online/streaming) learning using learningmachine in Python and R Aug 19, 2024
- Bayesian (nonlinear) adaptive learning Aug 12, 2024
- Auto XGBoost, Auto LightGBM, Auto CatBoost, Auto GradientBoosting Aug 5, 2024
- Copulas for uncertainty quantification in time series forecasting Jul 28, 2024
- Forecasting uncertainty: sequential split conformal prediction + Block bootstrap (web app) Jul 22, 2024
- learningmachine for Python (new version) Jul 15, 2024
- learningmachine v2.0.0: Machine Learning with explanations and uncertainty quantification Jul 8, 2024
- My presentation at ISF 2024 conference (slides with nnetsauce probabilistic forecasting news) Jul 3, 2024
- 10 uncertainty quantification methods in nnetsauce forecasting Jul 1, 2024
- Forecasting with XGBoost embedded in Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks Jun 24, 2024
- Forecasting Monthly Airline Passenger Numbers with Quasi-Randomized Neural Networks Jun 17, 2024
- Automated hyperparameter tuning using any conformalized surrogate Jun 9, 2024
- Recognizing handwritten digits with Ridge2Classifier Jun 3, 2024
- Forecasting the Economy May 27, 2024
- A detailed introduction to Deep Quasi-Randomized 'neural' networks May 19, 2024
- Probability of receiving a loan; using learningmachine May 12, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.18.2`: various examples and benchmarks with dimension reduction May 6, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.17.0`: boosting with Elastic Net, polynomials and heterogeneity in explanatory variables Apr 29, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.13.0`: taking into account inputs heterogeneity through clustering Apr 21, 2024
- mlsauce's `v0.12.0`: prediction intervals for LSBoostRegressor Apr 15, 2024
- Conformalized predictive simulations for univariate time series on more than 250 data sets Apr 7, 2024
- learningmachine v1.1.2: for Python Apr 1, 2024
- learningmachine v1.0.0: prediction intervals around the probability of the event 'a tumor being malignant' Mar 25, 2024
- Bayesian inference and conformal prediction (prediction intervals) in nnetsauce v0.18.1 Mar 18, 2024
- Multiple examples of Machine Learning forecasting with ahead Mar 11, 2024
- rtopy (v0.1.1): calling R functions in Python Mar 4, 2024
- ahead forecasting (v0.10.0): fast time series model calibration and Python plots Feb 26, 2024
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Part3: how many times do couples cheat on each other? Feb 19, 2024
- nnetsauce's introduction as of 2024-02-11 (new version 0.17.0) Feb 11, 2024
- Tuning Machine Learning models with GPopt's new version Part 2 Feb 5, 2024
- Tuning Machine Learning models with GPopt's new version Jan 29, 2024
- Subsampling continuous and discrete response variables Jan 22, 2024
- DeepMTS, a Deep Learning Model for Multivariate Time Series Jan 15, 2024
- A classifier that's very accurate (and deep) Pt.2: there are > 90 classifiers in nnetsauce Jan 8, 2024
- learningmachine: prediction intervals for conformalized Kernel ridge regression and Random Forest Jan 1, 2024
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Part2: how many times do couples cheat on each other? Descriptive analytics, interpretability and prediction intervals using conformal prediction Dec 25, 2023
- Diffusion models in Python with esgtoolkit (Part2) Dec 18, 2023
- Diffusion models in Python with esgtoolkit Dec 11, 2023
- Julia packaging at the command line Dec 4, 2023
- Quasi-randomized nnetworks in Julia, Python and R Nov 27, 2023
- A plethora of datasets at your fingertips Nov 20, 2023
- A classifier that's very accurate (and deep) Nov 12, 2023
- mlsauce version 0.8.10: Statistical/Machine Learning with Python and R Nov 5, 2023
- AutoML in nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized nnetworks) Pt.2: multivariate time series forecasting Oct 29, 2023
- AutoML in nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized nnetworks) Oct 22, 2023
- Version v0.14.0 of nnetsauce for R and Python Oct 16, 2023
- A diffusion model: G2++ Oct 9, 2023
- Diffusion models in ESGtoolkit + announcements Oct 2, 2023
- An infinity of time series forecasting models in nnetsauce (Part 2 with uncertainty quantification) Sep 25, 2023
- (News from) forecasting in Python with ahead (progress bars and plots) Sep 18, 2023
- Forecasting in Python with ahead Sep 11, 2023
- Risk-neutralize simulations Sep 4, 2023
- Comparing cross-validation results using crossval_ml and boxplots Aug 27, 2023
- Reminder Apr 30, 2023
- Did you ask ChatGPT about who you are? Apr 16, 2023
- A new version of nnetsauce (randomized and quasi-randomized 'neural' networks) Apr 2, 2023
- Simple interfaces to the forecasting API Nov 23, 2022
- A web application for forecasting in Python, R, Ruby, C#, JavaScript, PHP, Go, Rust, Java, MATLAB, etc. Nov 2, 2022
- Prediction intervals (not only) for Boosted Configuration Networks in Python Oct 5, 2022
- Boosted Configuration (neural) Networks Pt. 2 Sep 3, 2022
- Boosted Configuration (_neural_) Networks for classification Jul 21, 2022
- A Machine Learning workflow using Techtonique Jun 6, 2022
- Super Mario Bros © in the browser using PyScript May 8, 2022
- News from ESGtoolkit, ycinterextra, and nnetsauce Apr 4, 2022
- Explaining a Keras _neural_ network predictions with the-teller Mar 11, 2022
- New version of nnetsauce -- various quasi-randomized networks Feb 12, 2022
- A dashboard illustrating bivariate time series forecasting with `ahead` Jan 14, 2022
- Hundreds of Statistical/Machine Learning models for univariate time series, using ahead, ranger, xgboost, and caret Dec 20, 2021
- Forecasting with `ahead` (Python version) Dec 13, 2021
- Tuning and interpreting LSBoost Nov 15, 2021
- Time series cross-validation using `crossvalidation` (Part 2) Nov 7, 2021
- Fast and scalable forecasting with ahead::ridge2f Oct 31, 2021
- Automatic Forecasting with `ahead::dynrmf` and Ridge regression Oct 22, 2021
- Forecasting with `ahead` Oct 15, 2021
- Classification using linear regression Sep 26, 2021
- `crossvalidation` and random search for calibrating support vector machines Aug 6, 2021
- parallel grid search cross-validation using `crossvalidation` Jul 31, 2021
- `crossvalidation` on R-universe, plus a classification example Jul 23, 2021
- Documentation and source code for GPopt, a package for Bayesian optimization Jul 2, 2021
- Hyperparameters tuning with GPopt Jun 11, 2021
- A forecasting tool (API) with examples in curl, R, Python May 28, 2021
- Bayesian Optimization with GPopt Part 2 (save and resume) Apr 30, 2021
- Bayesian Optimization with GPopt Apr 16, 2021
- Compatibility of nnetsauce and mlsauce with scikit-learn Mar 26, 2021
- Explaining xgboost predictions with the teller Mar 12, 2021
- An infinity of time series models in nnetsauce Mar 6, 2021
- New activation functions in mlsauce's LSBoost Feb 12, 2021
- 2020 recap, Gradient Boosting, Generalized Linear Models, AdaOpt with nnetsauce and mlsauce Dec 29, 2020
- A deeper learning architecture in nnetsauce Dec 18, 2020
- Classify penguins with nnetsauce's MultitaskClassifier Dec 11, 2020
- Bayesian forecasting for uni/multivariate time series Dec 4, 2020
- Generalized nonlinear models in nnetsauce Nov 28, 2020
- Boosting nonlinear penalized least squares Nov 21, 2020
- Statistical/Machine Learning explainability using Kernel Ridge Regression surrogates Nov 6, 2020
- NEWS Oct 30, 2020
- A glimpse into my PhD journey Oct 23, 2020
- Submitting R package to CRAN Oct 16, 2020
- Simulation of dependent variables in ESGtoolkit Oct 9, 2020
- Forecasting lung disease progression Oct 2, 2020
- New nnetsauce Sep 25, 2020
- Technical documentation Sep 18, 2020
- A new version of nnetsauce, and a new Techtonique website Sep 11, 2020
- Back next week, and a few announcements Sep 4, 2020
- Explainable 'AI' using Gradient Boosted randomized networks Pt2 (the Lasso) Jul 31, 2020
- LSBoost: Explainable 'AI' using Gradient Boosted randomized networks (with examples in R and Python) Jul 24, 2020
- nnetsauce version 0.5.0, randomized neural networks on GPU Jul 17, 2020
- Maximizing your tip as a waiter (Part 2) Jul 10, 2020
- New version of mlsauce, with Gradient Boosted randomized networks and stump decision trees Jul 3, 2020
- Announcements Jun 26, 2020
- Parallel AdaOpt classification Jun 19, 2020
- Comments section and other news Jun 12, 2020
- Maximizing your tip as a waiter Jun 5, 2020
- AdaOpt classification on MNIST handwritten digits (without preprocessing) May 29, 2020
- AdaOpt (a probabilistic classifier based on a mix of multivariable optimization and nearest neighbors) for R May 22, 2020
- AdaOpt May 15, 2020
- Custom errors for cross-validation using crossval::crossval_ml May 8, 2020
- Documentation+Pypi for the `teller`, a model-agnostic tool for Machine Learning explainability May 1, 2020
- Encoding your categorical variables based on the response variable and correlations Apr 24, 2020
- Linear model, xgboost and randomForest cross-validation using crossval::crossval_ml Apr 17, 2020
- Grid search cross-validation using crossval Apr 10, 2020
- Documentation for the querier, a query language for Data Frames Apr 3, 2020
- Time series cross-validation using crossval Mar 27, 2020
- On model specification, identification, degrees of freedom and regularization Mar 20, 2020
- Import data into the querier (now on Pypi), a query language for Data Frames Mar 13, 2020
- R notebooks for nnetsauce Mar 6, 2020
- Version 0.4.0 of nnetsauce, with fruits and breast cancer classification Feb 28, 2020
- Create a specific feed in your Jekyll blog Feb 21, 2020
- Git/Github for contributing to package development Feb 14, 2020
- Feedback forms for contributing Feb 7, 2020
- nnetsauce for R Jan 31, 2020
- A new version of nnetsauce (v0.3.1) Jan 24, 2020
- ESGtoolkit, a tool for Monte Carlo simulation (v0.2.0) Jan 17, 2020
- Search bar, new year 2020 Jan 10, 2020
- 2019 Recap, the nnetsauce, the teller and the querier Dec 20, 2019
- Understanding model interactions with the `teller` Dec 13, 2019
- Using the `teller` on a classifier Dec 6, 2019
- Benchmarking the querier's verbs Nov 29, 2019
- Composing the querier's verbs for data wrangling Nov 22, 2019
- Comparing and explaining model predictions with the teller Nov 15, 2019
- Tests for the significance of marginal effects in the teller Nov 8, 2019
- Introducing the teller Nov 1, 2019
- Introducing the querier Oct 25, 2019
- Prediction intervals for nnetsauce models Oct 18, 2019
- Using R in Python for statistical learning/data science Oct 11, 2019
- Model calibration with `crossval` Oct 4, 2019
- Bagging in the nnetsauce Sep 25, 2019
- Adaboost learning with nnetsauce Sep 18, 2019
- Change in blog's presentation Sep 4, 2019
- nnetsauce on Pypi Jun 5, 2019
- More nnetsauce (examples of use) May 9, 2019
- nnetsauce Mar 13, 2019
- crossval Mar 13, 2019
- test Mar 10, 2019

Comments powered by Talkyard.