Today, give a try to Techtonique web app, a tool designed to help you make informed, data-driven decisions using Mathematics, Statistics, Machine Learning, and Data Visualization
A few weeks ago, I introduced a model-agnostic gradient boosting (XGBoost, LightGBM, CatBoost-like) procedure for supervised regression and classification, that can use any base learner (available in R and Python package mlsauce). You can find the previous posts here:
- https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2024/10/06/python/r/genericboosting
- https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2024/10/14/r/genericboosting-r
- https://thierrymoudiki.github.io/blog/2024/10/28/python/r/quasirandomizednn/histgenericboosting
LightGBM is widely used in the context of time series forecasting (see e.g for M5 forecasting competition and VN1 competition), and is based on decision trees. However, it’s possible to use many other base learners, such as ridge regression, kernel ridge regression, etc. In this post, I will show how to use mlsauce version 0.24.0 for time series forecasting, with any base learner.
1 - Hold-out set cross-validation
Here, Generic Gradient Boosting is compared to popular models such as VAR and VECM (without hyperparameter tuning), on the macrodata dataset from the statsmodels package. The dataset is split into a training set (90% of the data) and a testing set (10% of the data), and model performance is evaluated using Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and Winkler score (uncertainty quantification). Uncertainty quantification uses conformal prediction and numerical simulation as described in my paper, and more details can be found in these slides.
import mlsauce as ms
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.api as sm
try:
from statsmodels.tsa.base.datetools import dates_from_str
except ImportError:
ModuleNotFoundError
# some example data
mdata = sm.datasets.macrodata.load_pandas().data
# prepare the dates index
dates = mdata[['year', 'quarter']].astype(int).astype(str)
quarterly = dates["year"] + "Q" + dates["quarter"]
quarterly = dates_from_str(quarterly)
mdata = mdata[['realgovt', 'tbilrate', 'cpi']]
mdata.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(quarterly)
data = np.log(mdata).diff().dropna()
n = data.shape[0]
max_idx_train = np.floor(n*0.9)
training_index = np.arange(0, max_idx_train)
testing_index = np.arange(max_idx_train, n)
df_train = data.iloc[training_index,:]
df_test = data.iloc[testing_index,:]
regr_mts = ms.LazyBoostingMTS(verbose=0, ignore_warnings=True,
lags = 20, n_hidden_features=7, n_clusters=2,
type_pi="scp2-block-bootstrap",
#kernel="gaussian",
replications=250,
show_progress=False, preprocess=False,
sort_by="WINKLERSCORE",)
models = regr_mts.fit(df_train, df_test)
print(models[["RMSE", "WINKLERSCORE", "Time Taken"]].iloc[0:25,:])
0%| | 0/30 [00:00<?, ?it/s]100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:13<00:00, 2.20it/s]
RMSE WINKLERSCORE \
Model
MTS(GenericBooster(RidgeCV)) 0.32 1.71
MTS(GenericBooster(PassiveAggressiveRegressor)) 0.34 1.78
MTS(GenericBooster(SGDRegressor)) 0.32 1.87
MTS(GenericBooster(Ridge)) 0.35 1.93
MTS(GenericBooster(HuberRegressor)) 0.37 1.95
MTS(GenericBooster(ElasticNet)) 0.33 1.96
MTS(GenericBooster(Lasso)) 0.33 1.96
MTS(GenericBooster(DummyRegressor)) 0.33 1.96
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLars)) 0.33 1.96
MTS(GenericBooster(DecisionTreeRegressor)) 0.33 1.97
MTS(GenericBooster(QuantileRegressor)) 0.33 1.98
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLarsIC)) 0.33 1.99
MTS(GenericBooster(TweedieRegressor)) 0.33 2.01
MTS(GenericBooster(BayesianRidge)) 0.33 2.01
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoCV)) 0.33 2.02
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLarsCV)) 0.33 2.02
MTS(GenericBooster(LarsCV)) 0.33 2.02
MTS(GenericBooster(ElasticNetCV)) 0.33 2.02
MTS(GenericBooster(KNeighborsRegressor)) 0.33 2.03
MTS(GenericBooster(SVR)) 0.34 2.07
MTS(GenericBooster(ExtraTreeRegressor)) 0.33 2.19
VAR 0.33 2.21
VECM 0.34 2.39
MTS(GenericBooster(LinearSVR)) 0.45 3.03
MTS(GenericBooster(TransformedTargetRegressor)) 0.49 3.04
Time Taken
Model
MTS(GenericBooster(RidgeCV)) 0.13
MTS(GenericBooster(PassiveAggressiveRegressor)) 0.29
MTS(GenericBooster(SGDRegressor)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(Ridge)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(HuberRegressor)) 0.18
MTS(GenericBooster(ElasticNet)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(Lasso)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(DummyRegressor)) 0.08
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLars)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(DecisionTreeRegressor)) 0.11
MTS(GenericBooster(QuantileRegressor)) 0.15
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLarsIC)) 0.30
MTS(GenericBooster(TweedieRegressor)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(BayesianRidge)) 0.14
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoCV)) 5.01
MTS(GenericBooster(LassoLarsCV)) 0.54
MTS(GenericBooster(LarsCV)) 0.46
MTS(GenericBooster(ElasticNetCV)) 4.74
MTS(GenericBooster(KNeighborsRegressor)) 0.10
MTS(GenericBooster(SVR)) 0.09
MTS(GenericBooster(ExtraTreeRegressor)) 0.10
VAR 0.01
VECM 0.01
MTS(GenericBooster(LinearSVR)) 0.16
MTS(GenericBooster(TransformedTargetRegressor)) 0.13
2 - Individual examples
Here, I will show how to use mlsauce for time series forecasting, with Ridge regression and Kernel Ridge regression as base learners. 250 conformal predictive simulations are obtained, and the prediction is made for the next 20 periods.
import nnetsauce as ns
regr_ridge = ms.GenericBoostingRegressor(ms.RidgeRegressor(reg_lambda=1e3))
regr_krr = ms.GenericBoostingRegressor(ms.KRLSRegressor())
regr_mts = ns.MTS(regr_ridge, lags=20, replications=250,
type_pi="scp2-block-bootstrap")
regr_mts.fit(df_train)
regr_mts.predict(h=20)
regr_mts.plot('tbilrate')
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1612.53it/s]
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1678.79it/s]
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1663.07it/s]
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1298.61it/s]
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1410.21it/s]
100%|██████████| 46/46 [00:00<00:00, 1676.63it/s]
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:00<00:00, 13.82it/s]
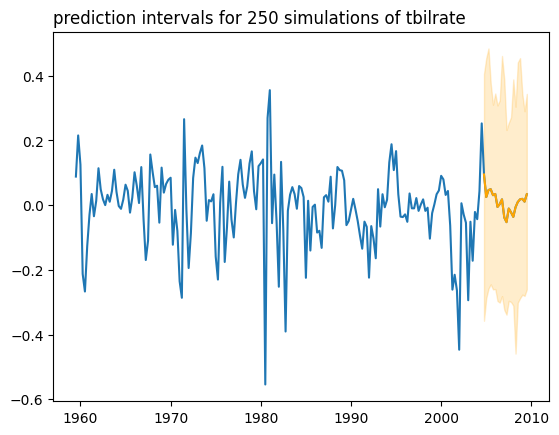
regr_mts = ns.MTS(regr_krr, lags=20, replications=250,
type_pi="scp2-block-bootstrap")
regr_mts.fit(df_train)
regr_mts.predict(h=20)
regr_mts.plot('tbilrate')
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 19.22it/s]
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 18.17it/s]
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 19.39it/s]
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 19.90it/s]
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 19.76it/s]
100%|██████████| 34/34 [00:01<00:00, 17.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:14<00:00, 4.76s/it]
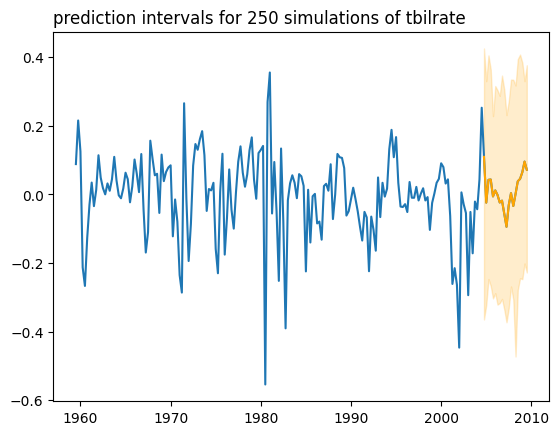
Comments powered by Talkyard.